Emerging Viruses: What We Know About Powassan Virus So Far
Stay informed about the latest emerging virus, Powassan virus, which can be transmitted through tick bites. Find out how to protect yourself from this potentially deadly disease.
Introduction:
The Powassan virus is a rare tick-borne disease that can cause severe health complications if left untreated. The virus is named after Powassan, a small town in Ontario, Canada, where the virus was first discovered in 1958. Since then, there have been cases of the Powassan virus reported in Canada, the United States, and Russia. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and prevention of the Powassan virus.
Causes of the Powassan virus:
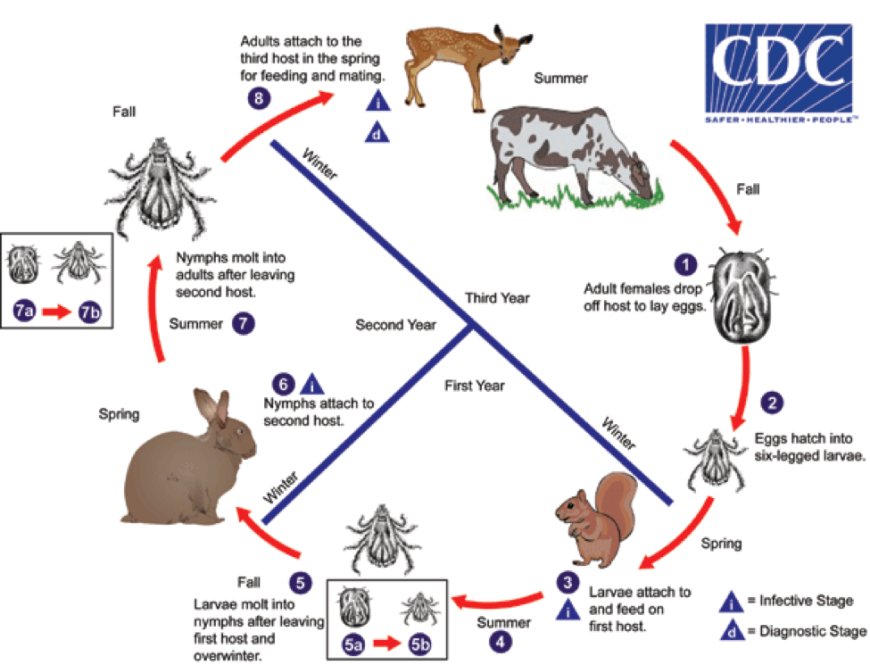
The Powassan virus is caused by the Powassan virus (POWV), which belongs to the Flaviviridae family of viruses. The virus is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. The two types of ticks that can transmit the Powassan virus are the black-legged tick (also known as the deer tick) and the groundhog tick.
Symptoms of the Powassan virus:
The symptoms of the Powassan virus can vary from person to person, and some people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, if symptoms do occur, they usually appear within 1 to 4 weeks after being bitten by an infected tick. Common symptoms of the Powassan virus include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Weakness
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Memory loss
- Difficulty speaking
If left untreated, the Powassan virus can lead to more severe health complications, such as inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or the lining of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis).
The risk factors for Powassan virus infection include:
- Geographical location: Powassan virus is primarily found in the northeastern United States and the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada. People living in or visiting these areas are at higher risk of being exposed to infected ticks.
- Outdoor activities: Spending time outdoors, particularly in wooded or grassy areas, increases the risk of tick bites and potential Powassan virus infection. Activities such as hiking, camping, and hunting may increase the risk of exposure to infected ticks.
- Tick bites: The Powassan virus is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. The risk of infection increases the longer the tick remains attached to the skin, so early detection and removal of ticks is important.
- Time of year: Powassan virus infection is most common in late spring, early summer, and mid-fall when ticks are most active.
- Age and health status: People with weakened immune systems, including the elderly and those with underlying medical conditions, may be more susceptible to severe disease if infected with Powassan virus.
It is important to take precautions to avoid tick bites when spending time outdoors, including wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent and checking for ticks regularly. If you develop symptoms of Powassan virus infection, such as fever, headache, and muscle weakness, seek medical attention immediately.
Complication
Powassan virus is a rare but potentially serious tick-borne virus that can cause severe neurological complications. Some of the complications associated with Powassan virus infection include:
- Encephalitis: This is inflammation of the brain, which can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, confusion, seizures, and coma. Encephalitis is a serious complication of Powassan virus infection and can be life-threatening.
- Meningitis: This is inflammation of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord, which can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, stiff neck, and sensitivity to light. Meningitis can be a complication of Powassan virus infection and can also be serious.
- Other neurological complications: Powassan virus infection can also lead to other neurological complications such as ataxia (loss of coordination), weakness, and paralysis. These complications can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Long-term effects: Some individuals who have had Powassan virus infection may experience long-term effects such as memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and fatigue.
It is important to note that not everyone who is infected with Powassan virus will experience complications, and some individuals may only have mild symptoms or no symptoms at all. However, it is important to seek medical attention if you have been bitten by a tick and develop any symptoms of Powassan virus infection.
Treatment
Here is currently no specific treatment for Powassan virus infection. Treatment is supportive and focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications.
If you have been diagnosed with Powassan virus infection, your healthcare provider may recommend the following:
- Hospitalization: If you have severe symptoms, such as encephalitis or meningitis, you may need to be hospitalized for supportive care, including intravenous fluids, medications to control seizures or pain, and breathing support if needed.
- Monitoring: Your healthcare provider may monitor you closely for any signs of complications and provide appropriate treatment if necessary.
- Rest and hydration: It is important to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection.
- Pain and fever relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers and fever reducers may be recommended to help relieve symptoms.
- Prevention of further tick bites: Your healthcare provider may advise you on ways to prevent further tick bites, such as wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent and avoiding areas where ticks are common.
It is important to seek medical attention if you have been bitten by a tick and develop any symptoms of Powassan virus infection. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes
Prevention of the Powassan virus:
Prevention is the best way to avoid contracting the Powassan virus. Here are some tips to help prevent tick bites:
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when spending time outdoors in wooded or grassy areas.
- Use insect repellent that contains DEET or picaridin.
- Check your body and clothing for ticks after spending time outdoors.
- Shower as soon as possible after spending time outdoors.
- Keep your yard clean and free of tall grass and brush.
- Check your pets for ticks, as they can also carry the Powassan virus.
If you do find a tick on your body, it is important to remove it as soon as possible. Use tweezers to grasp the tick as close to your skin as possible and pull it straight out. Do not twist or jerk the tick, as this can cause its mouthparts to break off and remain in your skin.
The Powassan virus is a serious disease that can cause severe health complications. It is important to take precautions when spending time outdoors to reduce your risk of contracting the disease. If you do experience symptoms of the Powassan virus after being bitten by a tick, seek medical attention immediately. With proper prevention and early treatment, you can protect yourself from the Powassan virus and enjoy a safe and healthy outdoor experience.
What's Your Reaction?