"Sarcoma: A Tale Of The Rare And Malignant"
Discover the courageous journey of a sarcoma survivor and gain insight into the diagnosis, treatment, and survival of this rare and malignant cancer. A must-read for anyone affected by sarcoma.
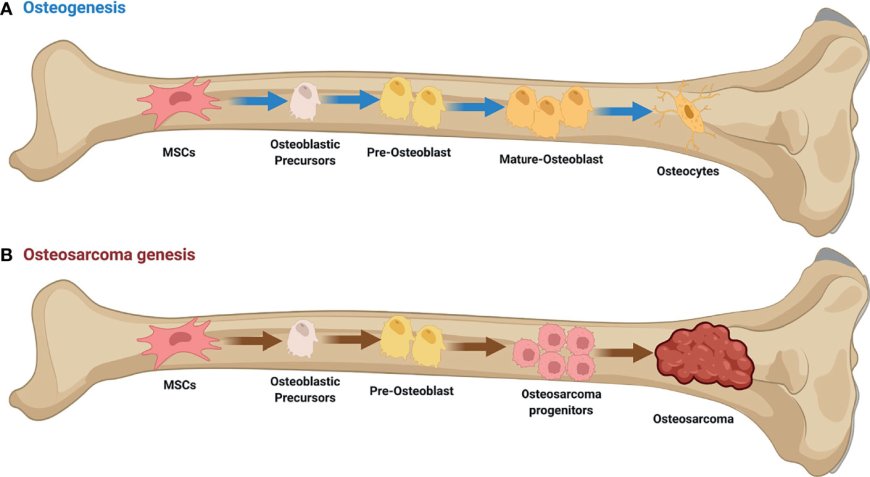
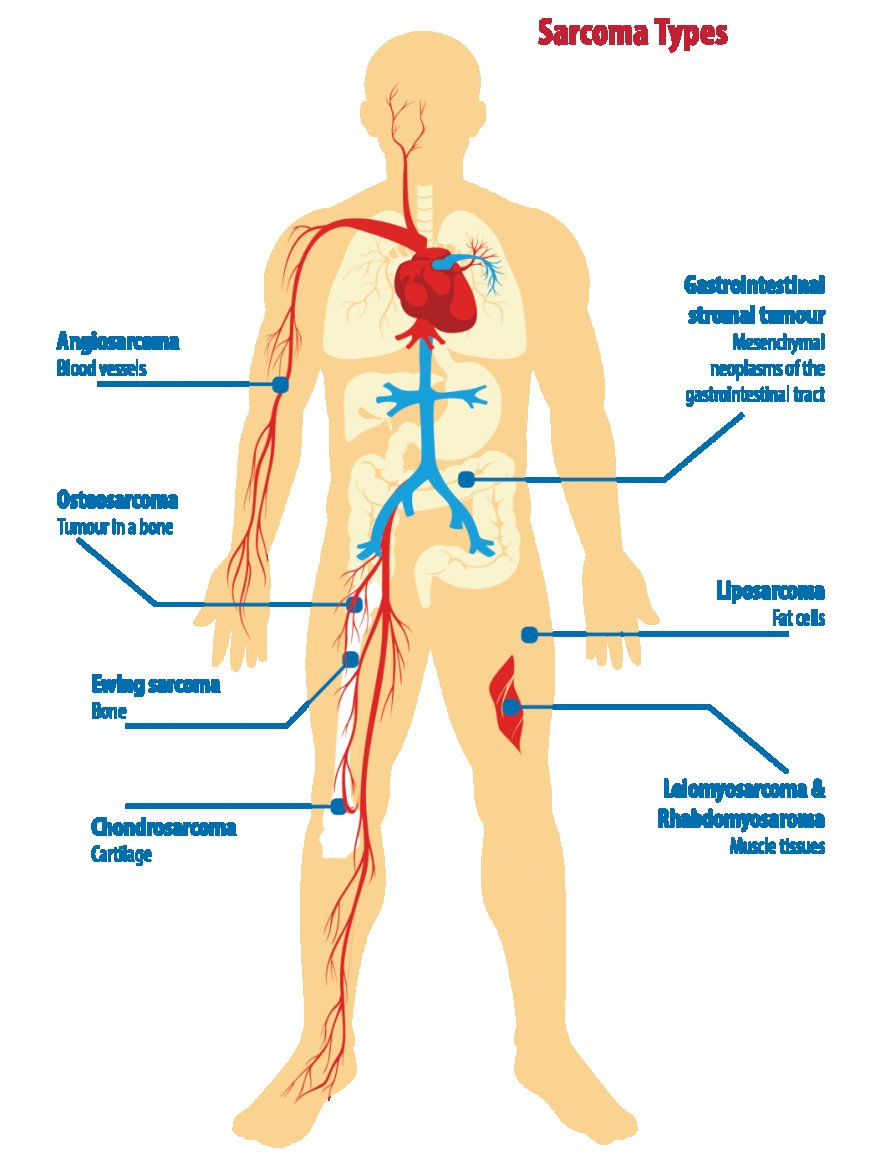
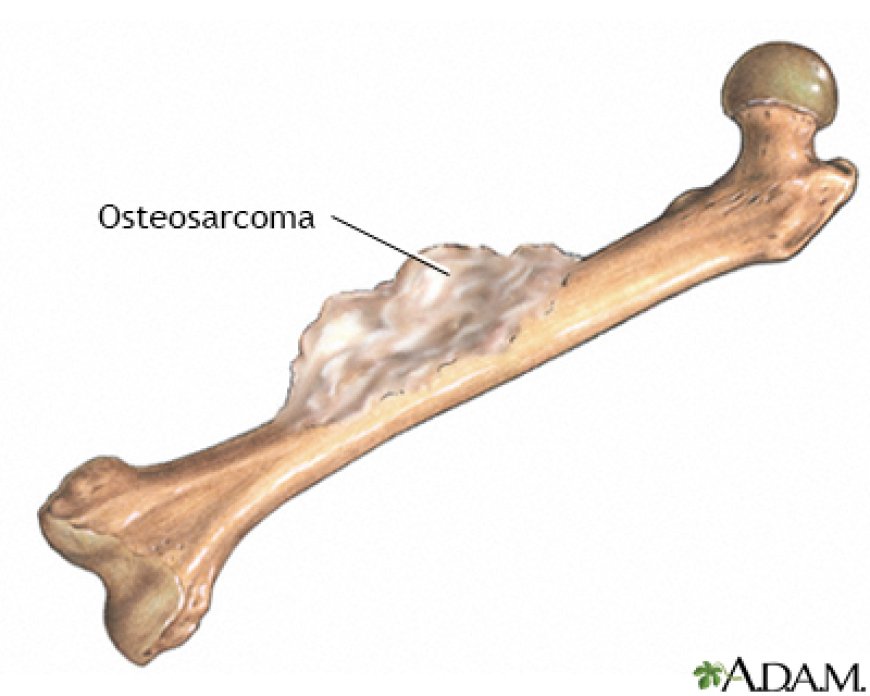
Sarcoma is a type of cancer that can develop in various locations of your body. The term sarcoma refers to a group of cancers that can develop in the bones and the soft tissues. Soft tissue sarcoma forms in the tissues that connect, support, and surround other body structures such as muscles, fat, blood vessels, nerves, tendons, and the lining of joints. There are more than 70 different types of sarcoma, and treatment varies based on sarcoma type, location, and other factors.
Causes of Sarcoma
It is not entirely clear what causes most sarcomas. Generally, cancer forms when mutations happen in the DNA within cells. The DNA inside a cell contains individual genes, each containing a set of instructions telling the cell what functions to perform, how to grow, and how to divide. Mutations can cause cells to grow and divide uncontrollably, leading to the accumulation of abnormal cells and the formation of a tumor. Cells can then break away and spread to other parts of the body (metastasize).
Symptoms of Sarcoma
Sarcoma symptoms can vary depending on the location and type of sarcoma. Some common symptoms include:
- A lump that can be felt through the skin, which may or may not be painful
- Bone pain
- A broken bone that occurs unexpectedly, with or without injury
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
Risk Factors
Some factors that can increase the risk of sarcoma include:
- Inherited syndromes: Some syndromes that increase the risk of cancer can be passed from parents to children. For instance, familial retinoblastoma and neurofibromatosis type 1 can increase the risk of sarcoma.
- Radiation therapy for cancer: Radiation treatment for cancer increases the risk of developing sarcoma later.
- Chronic swelling (lymphedema): Lymphedema is swelling caused by a backup of lymph fluid that occurs when the lymphatic system is blocked or damaged. It increases the risk of a type of sarcoma called angiosarcoma.
- Exposure to chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as some industrial chemicals and herbicides, can increase the risk of sarcoma that affects the liver.
- Exposure to viruses: The virus called human herpes virus 8 can increase the risk of a type of sarcoma called Kaposi's sarcoma in people with weakened immune systems.
Diagnosis Tests
Diagnosis and procedures used to diagnose sarcoma and determine its extent (stage) include:
- A physical exam: Your doctor will likely perform a physical exam to better understand your symptoms and look for other clues that will help with your diagnosis.
- Imaging tests: Which imaging tests are right for you will depend on your situation. Some tests, such as X-rays, are better for seeing bone problems. Other tests, such as MRI, are better for seeing connective tissue problems. Other imaging tests might include ultrasound, CT, bone scans, and positron emission tomography (PET) scans.
- Removing a sample of tissue for testing (biopsy): A biopsy is a procedure to remove a piece of suspicious tissue for lab testing. Sophisticated lab tests can determine whether the cells are cancerous and what kind of cancer they represent. Tests can also reveal information that's helpful for choosing the best treatments.
How a biopsy sample is collected depends on your particular situation. It could be removed with a needle passed through the skin or cut away during an operation. Sometimes a biopsy is done at the same time as surgery to remove the cancer. Once your doctor determines you have sarcoma, he or she might recommend additional tests to look for signs that the cancer has spread.
Treatment of Sarcoma:
The treatment of sarcoma depends on the location, size, and stage of the tumor. The most common treatments include:
Surgery:
Surgery is often the primary treatment for sarcoma. The goal of surgery is to remove all cancer cells from the affected area. Depending on the location and size of the sarcoma, this may require amputation of an arm or leg. However, surgeons always try to preserve limb function when possible. In some cases, it may not be possible to remove all cancer cells without damaging important structures, such as nerves or organs. In these situations, the surgeons work to remove as much of the sarcoma as possible.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy is another treatment option for sarcoma. This treatment uses high-powered energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. The radiation can come from a machine that moves around your body directing the beams of energy (external beam radiation). Or the radiation might be placed in your body temporarily (brachytherapy). Sometimes radiation is done during an operation to remove the cancer (intraoperative radiation).
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. Some types of sarcoma are more likely to respond to chemotherapy treatment than others. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to help destroy cancer cells that may have spread beyond the primary tumor site.
Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy is a drug treatment that uses medicines that attack specific weaknesses in cancer cells. Your doctor may have your sarcoma cells tested to see if they are likely to respond to targeted therapy drugs. This type of treatment is often used when chemotherapy is not effective or causes too many side effects.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy is a drug treatment that uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells. Immunotherapy drugs work by interfering with that process. This type of treatment is often used in advanced sarcoma cases where other treatments have not been effective.
Ablation Therapy:
Ablation therapy treatments destroy cancer cells by applying electricity to heat the cells, very cold liquid to freeze the cells or high-frequency ultrasound waves to damage the cell. This type of treatment is often used when surgery is not an option or as a palliative treatment to ease symptoms.
Prevention
There's no sure way to prevent sarcoma, but you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing the disease. These include:
1. Protecting your self from radiation exposure: Avoid unnecessary radiation exposure and make sure that medical procedures that use radiation, such as X-rays and CT scans, are necessary and the benefits outweigh the risks.
2. Avoiding harmful chemicals: Limit your exposure to harmful chemicals at work and at home.
3. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and not smoking can help reduce your risk of cancer.
4. Early detection: Being aware of the signs and symptoms of sarcoma can help with early detection and treatment. If you notice any unusual lumps or bumps, bone pain, or other symptoms, it's important to see your doctor right away.
Conclusion
Sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that can affect the bones and soft tissues in the body. There are more than 70 different types of sarcoma, and treatment depends on the type, location, and other factors. Symptoms of sarcoma can include lumps, bone pain, and weight loss. While the exact causes of most sarcomas are not clear, there are certain risk factors that can increase your chances of developing the disease. These include inherited syndromes, radiation therapy, exposure to chemicals, and viruses. There are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing sarcoma, including protecting yourself from radiation and chemicals, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of the disease. If you suspect that you may have sarcoma, it's important to see your doctor for a diagnosis and treatment plan. With early detection and proper treatment, the prognosis for sarcoma can be positive.
What's Your Reaction?