The Hidden Challenge: Understanding Diabetes Insipidus
Gain a deeper understanding of Diabetes Insipidus and find practical solutions to overcome its unique obstacles.
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a rare disorder characterized by the inability of the body to properly regulate water balance, leading to excessive thirst and urination. Unlike diabetes mellitus, which is more commonly known and often referred to simply as diabetes, diabetes insipidus is a distinct condition with its own set of causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
I. Understanding Diabetes Insipidus
A. Definition and Types
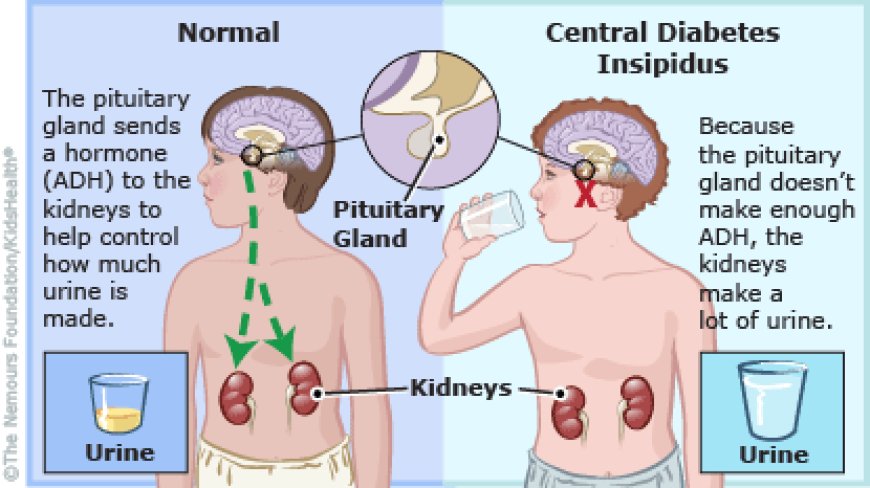
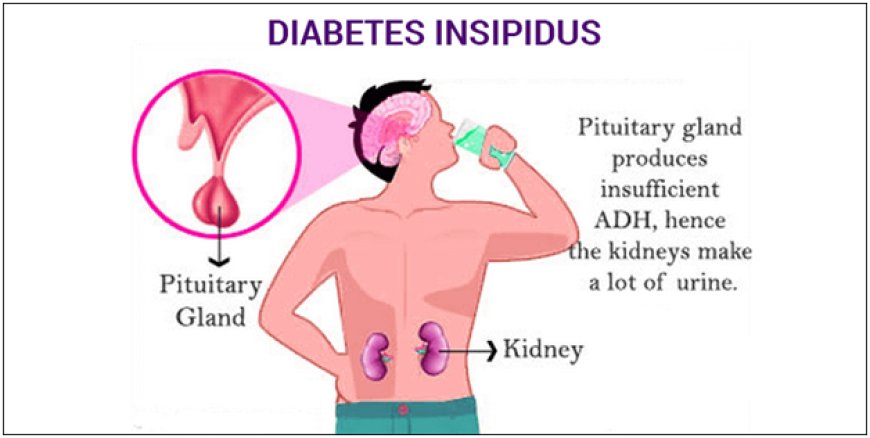
Diabetes insipidus is a hormonal disorder that disrupts the balance of water in the body. The condition is marked by an insufficient production or utilization of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin. ADH plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of water excreted by the kidneys.
There are two primary types of diabetes insipidus: central and nephrogenic. Central DI results from a deficiency of ADH, often due to damage to the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Nephrogenic DI, on the other hand, occurs when the kidneys fail to respond properly to ADH, despite normal secretion levels.
B. Causes and Risk Factors
1. Central Diabetes Insipidus:
Head trauma
Tumors affecting the pituitary gland or hypothalamus
Infections impacting the central nervous system
2. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus:
Genetic factors
Certain medications, such as lithium and some diuretics
Chronic kidney disease
II. Recognizing the Symptoms
A. Common Signs of Diabetes Insipidus
Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia): Individuals with diabetes insipidus often experience intense thirst due to the increased need for fluid replacement caused by excessive urination.
Frequent Urination (Polyuria): The hallmark symptom is the production of large volumes of dilute urine, leading to frequent trips to the bathroom.
Dehydration: Without adequate fluid intake, persistent dehydration may occur, resulting in symptoms like dry mouth, lethargy, and dizziness.
III. Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
A. Diagnostic Tests
Physicians use various tests to diagnose diabetes insipidus and differentiate it from other conditions:
Water Deprivation Test: This evaluates the body's ability to concentrate urine by restricting fluid intake.
Vasopressin Challenge Test: Administering synthetic vasopressin helps determine the type of DI by observing the response.
B. Differential Diagnosis
DI must be distinguished from other causes of excessive thirst and urination, such as uncontrolled diabetes mellitus or psychogenic polydipsia.
IV. Treatment Approaches
A. Central Diabetes Insipidus Treatment
1. Desmopressin: This synthetic form of ADH is a common treatment, usually administered as a nasal spray or oral medication.
2. Addressing Underlying Causes: Treating the root cause, such as surgical removal of tumors or managing infections, can resolve central DI.
B. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Management
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Increasing fluid intake and adjusting dietary salt intake can help manage symptoms.
2. Medications: Thiazide diuretics may be prescribed to enhance the kidneys' response to ADH.
V. Living with Diabetes Insipidus
A. Lifestyle Considerations
Managing diabetes insipidus involves ongoing lifestyle adjustments:
Hydration: Maintaining adequate fluid intake is crucial to prevent dehydration.
Monitoring Symptoms: Regularly assessing thirst, urine output, and overall well-being helps individuals and healthcare providers manage the condition effectively.
VI. Research and Future Perspectives
Research into diabetes insipidus continues to explore novel treatment options and gain a deeper understanding of the genetic and molecular factors contributing to the disorder. Ongoing studies aim to improve diagnostic techniques and enhance the quality of life for those affected by this rare condition.
VIII. Coping with Challenges.
A. Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with diabetes insipidus can present emotional challenges due to the constant need for monitoring and adaptation. Individuals may find support through counseling or joining patient advocacy groups to share experiences and coping strategies.
B. Pediatric Considerations
Children with diabetes insipidus may face unique challenges. Parents and caregivers play a vital role in ensuring proper hydration, medication administration, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers.
IX. Addressing Common Misconceptions
A. Distinction from Diabetes Mellitus
It's crucial to emphasize the distinction between diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus. Despite sharing the term "diabetes," these conditions have different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
B. Rare, but Not Unmanageable
While diabetes insipidus is considered rare, awareness is key to prompt diagnosis and effective management. Collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, and researchers is essential for enhancing understanding and treatment options.
X. Patient Perspectives and Stories
A. Personal Narratives
Hearing from individuals living with diabetes insipidus can provide valuable insights. Stories of resilience, adaptation, and successful management contribute to a sense of community and support for others facing similar challenges.
XI. The Role of Research and Innovation
A. Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research explores potential advancements, including targeted therapies and gene-based interventions. Collaborative efforts among scientists, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies aim to improve treatment outcomes and expand the understanding of this complex disorder.
B. Genetic Insights
As genetic research progresses, identifying specific gene mutations associated with diabetes insipidus may lead to personalized treatment approaches, offering a more tailored and effective response.
XII. Global Perspectives on Diabetes Insipidus
A. Access to Diagnosis and Treatment
While awareness and resources for diabetes insipidus are more established in some regions, global efforts are essential to ensure access to accurate diagnosis and optimal treatment worldwide.
B. Support Networks
International collaborations and online support communities contribute to a global network of individuals sharing information, experiences, and advice.
XIII. Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Diabetes Insipidus
In conclusion, diabetes insipidus is a rare yet significant medical condition impacting the lives of those affected. Through continued research, awareness campaigns, and patient advocacy, strides are being made to enhance diagnosis, treatment options, and overall quality of life for individuals with diabetes insipidus. The collaborative efforts of healthcare professionals, researchers, patients, and support networks play a pivotal role in shaping a future where this condition is not just manageable but better understood and, ultimately, preventable.
As we move forward, the spotlight on diabetes insipidus should grow brighter, fostering a comprehensive understanding within the medical community and beyond. With advancements in science, increased awareness, and a shared commitment to addressing this rare disorder, the journey toward improved outcomes for those living with diabetes insipidus continues.
Discover the enigmatic world of Diabetes Insipidus and unravel the mysteries of this hidden challenge together. Delve into its depths and uncover the secrets of its manifestation. Let's embark on this passionate journey of understanding and conquering Diabetes Insipidus, hand in hand.
What's Your Reaction?