"The Silent Killer: Tuberculosis And Its Impact On Global Health"
Tuberculosis is a leading cause of death worldwide. Discover the impact of this disease on global health and the challenges it presents for public health officials.
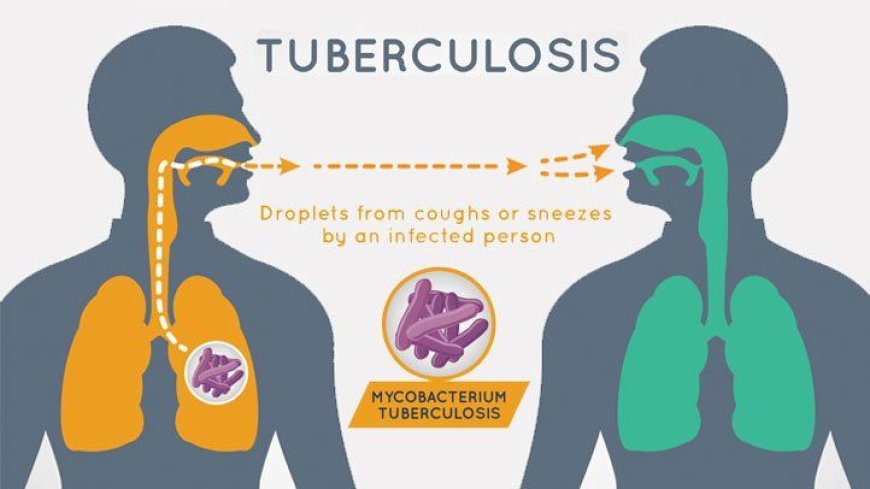
Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB, is a highly infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs but can also target other parts of the body. The bacterium responsible for this disease is Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is transmitted through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Despite significant progress in the global fight against TB, it remains a major public health concern, especially in developing countries. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), TB was responsible for around 1.4 million deaths worldwide in 2019 alone. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of tuberculosis.
Causes of Tuberculosis
As mentioned earlier, TB is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium. The disease spreads from person to person through the air when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, speaks, or spits. This bacterium can survive for several hours in the air and can be inhaled by healthy people who share the same environment with infected individuals.
Once the bacteria enter the body, they can remain dormant for years and cause no harm. This condition is known as latent TB infection. However, if the immune system becomes weakened, the bacteria can become active and start multiplying, leading to active TB disease.
Risk Factors for Tuberculosis
Several factors increase the risk of developing TB disease. These include:
- Weak immune system: Individuals with weak immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, malnutrition, or those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation, are more vulnerable to TB.
- Close contact with an infected person: People who live or work with TB-infected individuals are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
- Age: TB is more common among older adults and young children.
- Poor living conditions: Overcrowding, poor ventilation, and inadequate nutrition increase the risk of TB transmission.
Symptoms of TB
The symptoms of TB can vary depending on the part of the body affected. The most common symptoms of pulmonary TB include:
- Persistent cough that lasts for more than three weeks
- Chest pain
- Fever and chills
- Night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
If the bacteria have spread to other parts of the body, the symptoms may include:
- Back pain
- Joint pain
- Headaches
- Confusion
- Seizures
Diagnosis
Diagnosing TB involves a combination of several tests. The first step is usually a physical examination and medical history review. The doctor may also order a chest X-ray, sputum test, and blood tests.
If these tests are inconclusive, the doctor may recommend a bronchoscopy or biopsy to obtain a tissue sample for analysis. In some cases, a skin test or a tuberculosis blood test may also be used to diagnose the disease.
Treatment of tuberculosis.
Treating TB usually involves a combination of antibiotics that are taken for several months. The standard treatment regimen for drug-susceptible TB involves a combination of four antibiotics taken daily for two months, followed by two antibiotics taken for four to six months.
Drug-resistant TB is more challenging to treat and requires a longer and more intensive treatment regimen. Treatment for drug-resistant TB may involve taking several medications for up to two years.
Prevention of Tuberculosis
Preventing the spread of TB requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Vaccination: The Bacilli Chalmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine can provide partial protection against TB.
- Early detection and treatment: Early detection and treatment of TB can prevent the spread of the disease.
- Infection control measures: Measures such as proper ventilation and cough etiquette can reduce the
- Screening of high-risk individuals: Individuals, who are at high risk of developing TB, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those who work in healthcare settings, should be screened regularly for TB.
- Improved living conditions: Overcrowding, poor ventilation, and inadequate nutrition increase the risk of TB transmission. Improving living conditions can reduce the spread of TB.
Complication
Tuberculosis (TB) can lead to various complications if left untreated or if not properly managed. Some of the common complications of TB include:
- Spread of infection: TB is a highly contagious disease that can spread from the lungs to other parts of the body, such as the brain, kidneys, or spine. This can cause severe complications and may even be life-threatening.
- Respiratory failure: Severe TB infection can cause respiratory failure, which is a condition where the lungs can no longer provide enough oxygen to the body. This can be fatal if not treated promptly.
- Miliary TB: Miliary TB is a form of the disease that occurs when the TB bacteria spread throughout the body and form tiny nodules or lesions in various organs. This can cause symptoms such as fever, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Spinal TB: Spinal TB is a type of TB that affects the spine and can cause back pain, spinal deformities, and even paralysis in severe cases.
- Drug-resistant TB: If TB is not properly treated or if the patient fails to complete the full course of antibiotics, drug-resistant strains of TB can develop. This can be much harder to treat and may require longer and more intensive treatment regimens.
- HIV co-infection: HIV weakens the immune system, making individuals with HIV more susceptible to TB. Conversely, TB can also make HIV progression faster, leading to AIDS.
- Social isolation and stigma: TB can lead to social isolation and stigma, which can have a significant impact on a patient's mental health and quality of life.
Conclusion
TB remains a significant global health concern, especially in developing countries. It is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium and spreads through the air when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. Symptoms of TB include persistent cough, chest pain, fever, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves a combination of several tests, and treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics taken for several months. Preventing the spread of TB requires a comprehensive approach that includes vaccination, early detection and treatment, infection control measures, screening of high-risk individuals, and improving living conditions.
What's Your Reaction?