“Advances in Colon Cancer Research: New Treatments and Future Directions”
Discover the latest advances in colon cancer research, including new treatments and future directions. Find out how researchers are working to improve outcomes for people with this disease.
Colon cancer is a serious disease that can affect people of all ages. While it is more commonly diagnosed in older adults, younger people can also develop the disease. A recent study has identified four "red flag" symptoms of colon cancer in younger people, which can help with early detection and treatment.
Cause
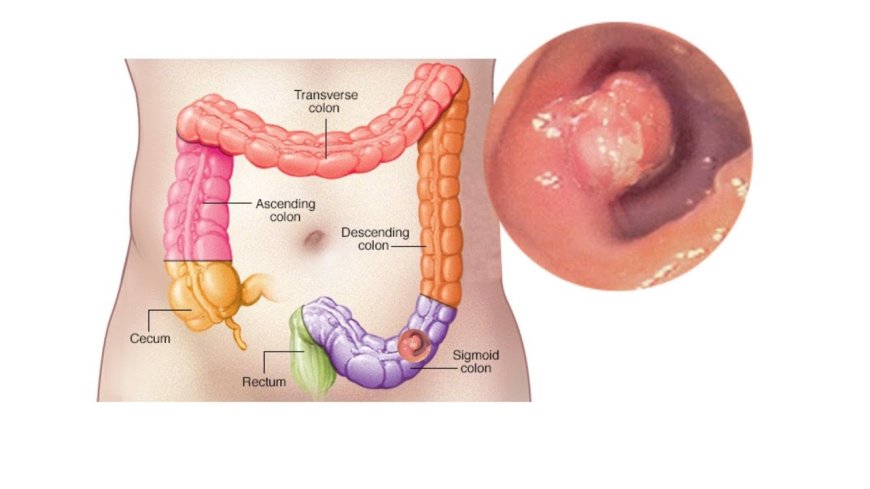
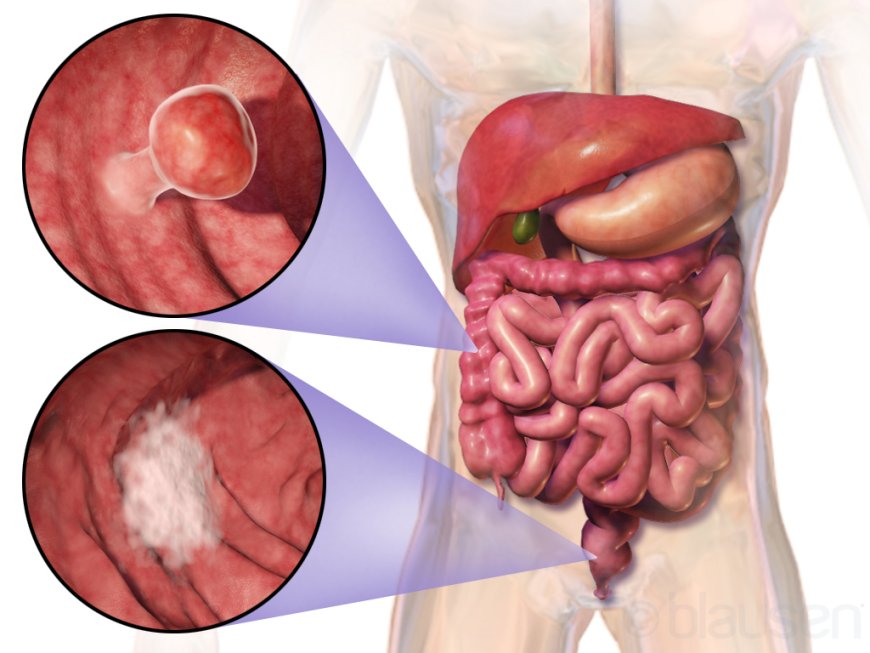
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, typically arises from the abnormal growth of cells in the lining of the colon or rectum. The exact cause of colon cancer is not known, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms
The four symptoms are:
Rectal bleeding: This is one of the most common symptoms of colon cancer in people of all ages, but it is especially concerning in younger people who do not have a history of hemorrhoids or other gastrointestinal issues.
Abdominal pain: Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort that does not go away with over-the-counter pain medication is another red flag symptom of colon cancer.
Change in bowel habits: A sudden and unexplained change in bowel habits, such as alternating between diarrhea and constipation, can be a sign of colon cancer.
Anemia: A decrease in red blood cells caused by colon cancer can result in anemia. Symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it is essential to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early detection and treatment are crucial in improving outcomes for colon cancer patients, regardless of age.
Risk factors
It is also important to note that certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing colon cancer. These include a family history of the disease, a personal history of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a diet high in processed or red meats, obesity, and smoking.
While colon cancer screening is typically recommended for individuals over the age of 50, younger individuals who have symptoms or risk factors may also benefit from screening. This can include a colonoscopy, which is a procedure that allows a doctor to examine the entire colon and remove any polyps or abnormal growths.
In addition to screening, individuals can also take steps to reduce their risk of colon cancer. This includes maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
The four "red flag" symptoms of colon cancer in younger people are rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, change in bowel habits, and anemia. While these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, it is essential to seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time. By identifying symptoms early and taking steps to reduce risk, individuals can improve their chances of successful treatment and recovery from colon cancer.
Complications
Colon cancer can lead to various complications, especially if left untreated or undiagnosed. Some of the potential complications of colon cancer include:
Spread of cancer: Colon cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, lungs, or bones. When this happens, it is known as metastatic colon cancer, and it can be more challenging to treat.
Intestinal obstruction: If a tumor in the colon becomes large enough, it can block the intestine and prevent stool from passing through. This can cause abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
Perforation of the colon: In rare cases, a tumor in the colon can cause a hole or perforation in the wall of the colon. This can cause severe abdominal pain, fever, and signs of infection.
Bleeding: Colon cancer can cause bleeding, which can lead to anemia and other complications.
Surgery complications: Surgery to remove the tumor or part of the colon can lead to complications such as infection, bleeding, and bowel obstruction.
Emotional impact: A diagnosis of colon cancer can also have a significant emotional impact on a person and their loved ones. Anxiety, depression, and stress are common emotional responses to a cancer diagnosis.
It is important to note that early detection and treatment of colon cancer can reduce the risk of complications. Regular screening and following a healthy lifestyle can help prevent the development of colon cancer or detect it at an early stage when it is easier to treat. If you experience any symptoms of colon cancer, it is important to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of colon cancer
The treatment for colon cancer depends on various factors such as the stage of the cancer, the size and location of the tumor, the patient's overall health, and their preferences. The standard treatment options for colon cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these.
Surgery: Surgery is the primary treatment for colon cancer. The surgeon will remove the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue. The amount of colon removed depends on the size and location of the tumor. After the surgery, the remaining healthy parts of the colon will be reconnected, and the patient can usually resume normal bowel function.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy may be given before or after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence or to treat metastatic colon cancer.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams of radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be given before or after surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence, or it may be used to relieve symptoms of advanced colon cancer.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that target specific proteins or genes that promote the growth of cancer cells. Targeted therapy may be used in combination with chemotherapy for advanced colon cancer.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a newer treatment option that works by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells. Immunotherapy may be used for advanced colon cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
The treatment plan will be tailored to each individual patient based on their specific circumstances. It is essential to discuss the treatment options with a healthcare provider and to ask any questions or voice any concerns about the treatment. Support from family, friends, and support groups can also be helpful during the treatment process.
Conclusions
Early detection, effective treatment, and prevention strategies can significantly improve the outlook for individuals with colon cancer.
What's Your Reaction?