Lupus 101: What You Need to Know About this Autoimmune Disease
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with lupus, it's important to understand what the disease is and how it can be managed. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of lupus and practical tips for coping with the condition.
Lupus, also known as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease that affects around 5 million people globally. This chronic condition occurs when the body's immune system attacks its own tissues and organs, leading to inflammation and damage. Lupus can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs.
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Here are some factors that may contribute to the development of lupus:
- Genetics: Lupus can run in families, and certain genes may make people more susceptible to developing the disease.
- Hormones: Lupus is more common in women than men, and hormonal changes such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause may contribute to the development of the disease.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors such as ultraviolet light, infections, and certain medications can trigger lupus or make symptoms worse.
- Immune system dysfunction: Lupus is an autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the body. It's not clear why this happens, but it's thought to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as viral infections, can trigger lupus or make symptoms worse.
It's important to note that not everyone with these risk factors will develop lupus, and some people with lupus may not have any known risk factors. The exact cause of lupus is still being studied, and researchers are working to identify additional factors that may contribute to the development of the disease.
Symptoms of lupus
The symptoms of lupus can vary widely from person to person and may come and go over time. Some common symptoms of lupus include:
- Joint pain and swelling: Lupus can cause inflammation and pain in the joints, particularly in the hands, wrists, and knees.
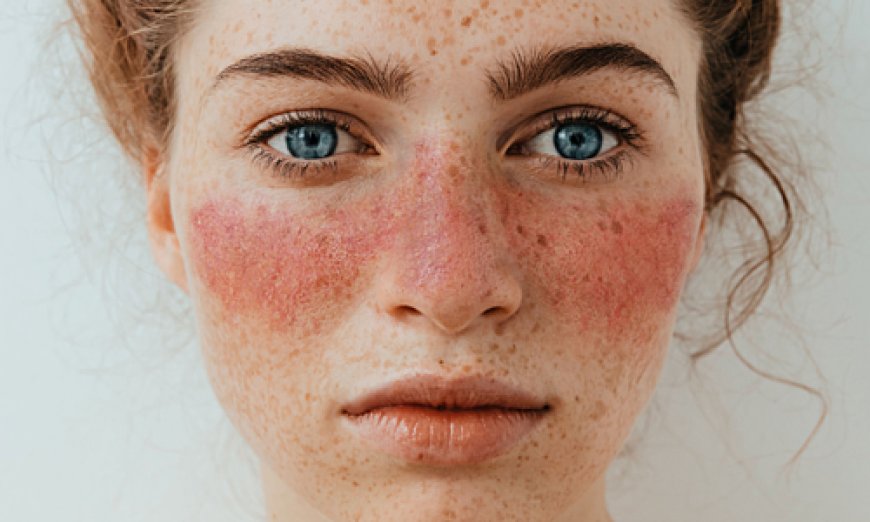
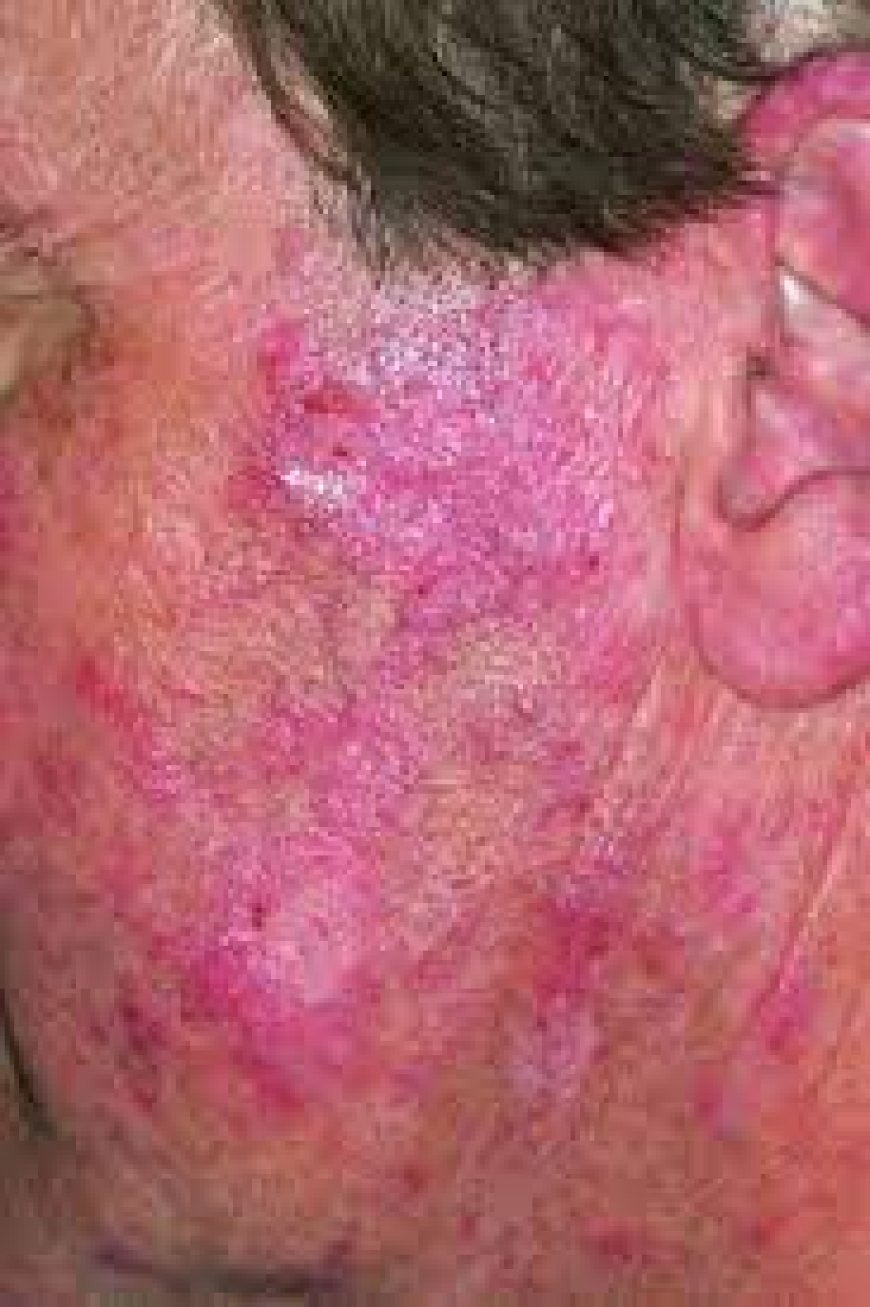
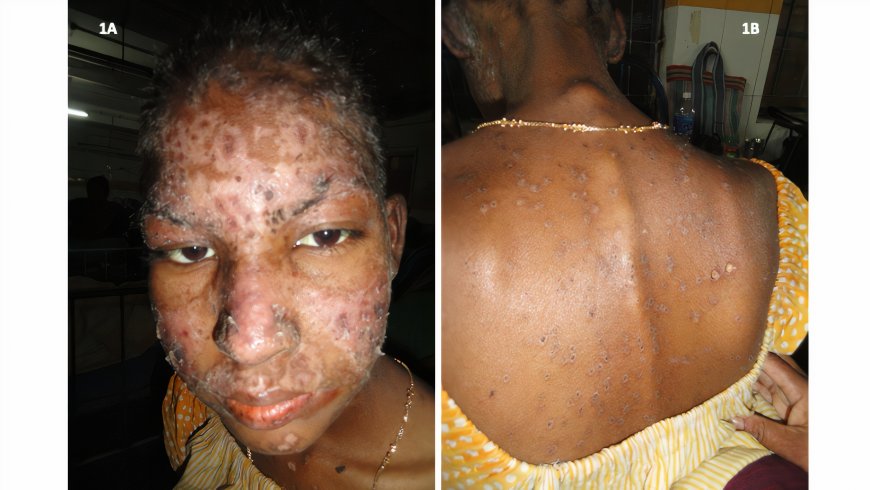
- Skin rashes: Many people with lupus develop a butterfly-shaped rash on their face that covers the cheeks and bridge of the nose. Other types of skin rashes may also occur, particularly in areas exposed to sunlight.
- Fatigue: People with lupus often experience persistent fatigue, even after getting enough rest.
- Fever: Lupus can cause a low-grade fever that comes and goes.
- Hair loss: Lupus can cause hair to become brittle and fall out.
- Sensitivity to sunlight: People with lupus may be more sensitive to sunlight and develop skin rashes or other symptoms after exposure to the sun.
- Mouth sores: Lupus can cause sores or ulcers in the mouth or nose that are painful and don't heal easily.
- Raynaud's phenomenon: Lupus can cause the fingers and toes to turn white or blue in response to cold or stress.
- Chest pain: Lupus can cause inflammation in the lining of the heart or lungs, leading to chest pain or difficulty breathing.
- Headaches and confusion: Lupus can affect the brain and nervous system, leading to headaches, confusion, memory loss, and other neurological symptoms.
It's important to note that these symptoms can be caused by other conditions as well, so it's important to see a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment of lupus can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
When to see doctor
It's important to see a doctor if you are experiencing any symptoms that may be associated with lupus or if you have any concerns about your risk for the disease. Some signs and symptoms that may warrant a visit to the doctor include:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Joint pain, swelling, or stiffness
- Skin rashes, especially those that are sensitive to sunlight
- Unexplained fever
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Headaches, confusion, or seizures
- Digestive problems, such as abdominal pain or nausea
- Changes in vision or eye pain
- Mouth sores or ulcers that won't heal
- Unexplained hair loss
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it's important to make an appointment with your healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment of lupus can help prevent complications and improve outcomes. Your healthcare provider may order blood tests or other diagnostic tests to determine if you have lupus or another underlying condition. They can also help develop a treatment plan to manage your symptoms and improve your overall health.
Risk factors
There are several risk factors associated with the development of lupus, including:
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop lupus, with the disease being diagnosed in women 9 times more often than men.
- Age: Lupus can affect people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 15 and 45.
- Genetics: Genetics can play a role in the development of lupus, as the disease tends to run in families. However, it's important to note that having a family member with lupus doesn't necessarily mean you will develop the disease.
- Ethnicity: Lupus is more common among people of African, Asian, and Hispanic descent than in Caucasians.
- Environmental factors: Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to ultraviolet light, infections, and medications, may trigger the development of lupus in people who are genetically susceptible.
- Hormones: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, may trigger or worsen lupus symptoms in some people.
It's important to note that having one or more of these risk factors doesn't necessarily mean you will develop lupus. However, if you have concerns about your risk of developing the disease, it's important to talk to your healthcare provider.
Complications
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, and if left untreated or poorly managed, it can lead to several complications. Some of the common complications of lupus include:
- Kidney damage: Lupus can cause inflammation in the kidneys, leading to kidney damage or failure. This is known as lupus nephritis.
- Cardiovascular disease: People with lupus are at higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks and strokes, due to inflammation and damage to blood vessels.
- Infections: Lupus can weaken the immune system, making people more susceptible to infections such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections.
- Osteoporosis: People with lupus are at higher risk of developing osteoporosis, a condition that causes bones to become weak and brittle, due to the use of steroids to manage symptoms.
- Pregnancy complications: Women with lupus are at higher risk of pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia and miscarriage.
- Lung damage: Lupus can cause inflammation and scarring in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced lung function.
- Central nervous system complications: Lupus can affect the brain and nervous system, leading to seizures, psychosis, and other neurological symptoms.
It's important for people with lupus to work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their symptoms and prevent complications. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and other diagnostic tests can help detect complications early, allowing for prompt treatment and better outcomes.
Treatment
There is no cure for lupus, but treatment can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. Treatment for lupus typically depends on the severity and type of symptoms, as well as the person's overall health and medical history. Here are some common treatments for lupus:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with lupus.
- Corticosteroids: These medications can help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, which can help manage symptoms of lupus. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can cause side effects such as weight gain, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
- Antimalarials: These medications, such as hydroxychloroquine, can help reduce skin rashes and joint pain associated with lupus. They may also reduce the risk of flares and help protect against organ damage.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications can help suppress the immune system and prevent it from attacking healthy tissues. They may be used to treat severe lupus symptoms or to prevent organ damage.
- Biologics: These medications target specific proteins involved in the immune system response and can help reduce inflammation associated with lupus. They may be used in people with severe lupus symptoms who do not respond to other treatments.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding exposure to sunlight can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of flares.
It's important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that's tailored to individual needs and preferences. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help monitor symptoms and adjust treatment as needed.
What's Your Reaction?