Bladder Cancer: Understanding the Silent Killer
Gain a comprehensive understanding of bladder cancer, often referred to as the "silent killer," including its symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how early detection and awareness play crucial roles in combating this disease.
Bladder cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of bladder cancer, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By staying informed about bladder cancer, you can make educated decisions regarding prevention, early detection, and treatment if necessary. Now, let's dive deeper into the world of bladder cancer and empower ourselves with knowledge to protect our health.
What is Bladder Cancer?
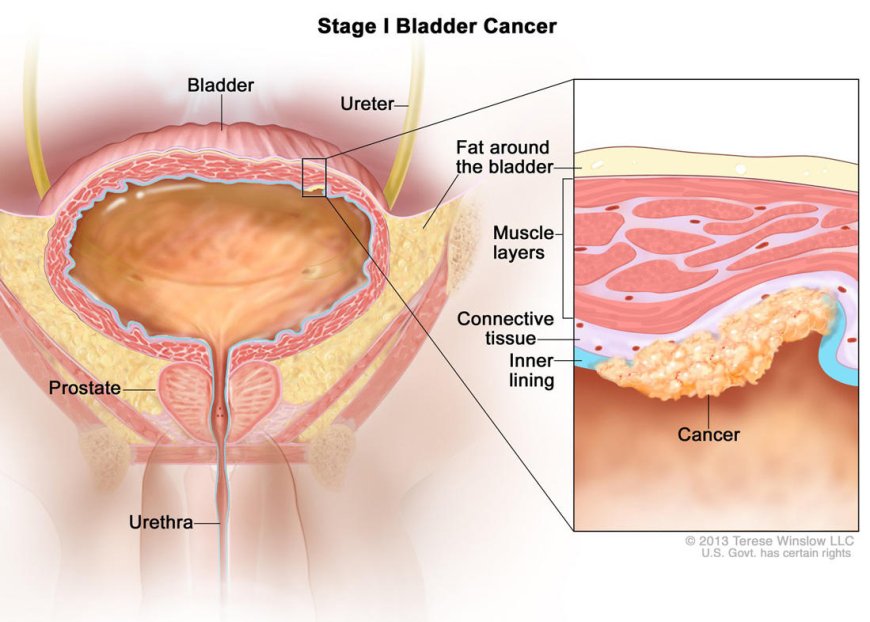
Bladder cancer refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the lining of the bladder. This type of cancer can develop due to various factors such as smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, chronic bladder inflammation, and family history of the disease. There are different types of bladder cancer, including transitional cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. The most common type is transitional cell carcinoma, which starts in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Smoking is the leading cause of bladder cancer, accounting for approximately half of all cases. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can enter the bloodstream and eventually reach the bladder, causing damage to the cells. Other risk factors include exposure to certain chemicals and substances such as arsenic, diesel exhaust, and certain medications. Chronic bladder inflammation, often caused by urinary tract infections or bladder stones, can also increase the risk of developing bladder cancer. Additionally, individuals with a family history of bladder cancer are more likely to develop the disease.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Bladder Cancer
One of the challenges of bladder cancer is that it often does not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, certain symptoms may start to appear. The most common symptom is blood in the urine, which may appear pink, red, or brown. Other symptoms include frequent urination, pain during urination, and lower back pain. It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other health conditions, so it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Early detection of bladder cancer is vital for successful treatment and improved outcomes. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Your doctor may recommend various diagnostic tests and procedures to determine the presence of bladder cancer.
Diagnosing Bladder Cancer - Tests and Procedures
To diagnose bladder cancer, your doctor may start with a urine test to check for the presence of blood or cancer cells in the urine. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, may be performed to visualize the bladder and identify any abnormalities. In some cases, a procedure called cystoscopy may be recommended. During a cystoscopy, a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to examine the bladder lining for any signs of cancer.
If bladder cancer is detected, further tests may be conducted to determine the stage and severity of the disease. These tests may include additional imaging studies, such as a bone scan or chest X-ray, to check if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
The treatment of bladder cancer depends on various factors, including the stage and grade of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Surgery is a common treatment for bladder cancer and may involve removing the tumor from the bladder (transurethral resection) or removing the entire bladder (radical cystectomy). In some cases, a new bladder can be created using a segment of the intestine.
Chemotherapy may be used before or after surgery to destroy cancer cells or to shrink tumors. Radiation therapy, on the other hand, uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing. Immunotherapy and targeted therapy are newer treatment approaches that aim to boost the body's immune system or target specific molecules in cancer cells, respectively.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, and it is important to discuss the options with your healthcare team to determine the most suitable approach for your specific case.
Living with Bladder Cancer - Support and Lifestyle Changes
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming, and it is important to have a strong support system in place. Your healthcare team can provide guidance and support throughout your treatment journey. Additionally, joining support groups or seeking counseling can help you cope with the emotional and psychological impact of the disease.
Making certain lifestyle changes can also contribute to your overall well-being. Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy diet, staying physically active and managing stress can all play a role in supporting your body's ability to fight against cancer and improve your quality of life.
Prevention and Reducing the Risk of Bladder Cancer
While it may not be possible to prevent bladder cancer entirely, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to lower your chances of developing bladder cancer. Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and substances, such as those found in certain workplaces or industries can also help reduce the risk. Additionally, maintaining good bladder health by drinking plenty of fluids and practicing good hygiene can contribute to overall bladder health.
Bladder Cancer Research and Advancements
Ongoing research and advancements in the field of bladder cancer have led to improved treatment options and outcomes for patients. Clinical trials are being conducted to test new drugs and therapies that may offer better results or fewer side effects. It is important for patients to stay informed about the latest developments in bladder cancer research and discuss with their healthcare team if they may be eligible to participate in clinical trials.
Conclusion
Bladder cancer is a complex disease that requires a comprehensive understanding to effectively prevent, detect, and treat. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and seek early medical attention if necessary. With advancements in diagnosis and treatment, the prognosis for bladder cancer has improved significantly. However, it is important to stay vigilant and prioritize regular check-ups to ensure early detection and timely intervention. By staying informed and empowered, we can continue to fight against bladder cancer and protect our health.
What's Your Reaction?