"The Fight Against Stomach Cancer: Stories Of Hope And Survival"
Despite its reputation as a deadly disease, many people with stomach cancer go on to live full and productive lives. Hear from survivors and learn how they overcame this formidable opponent.
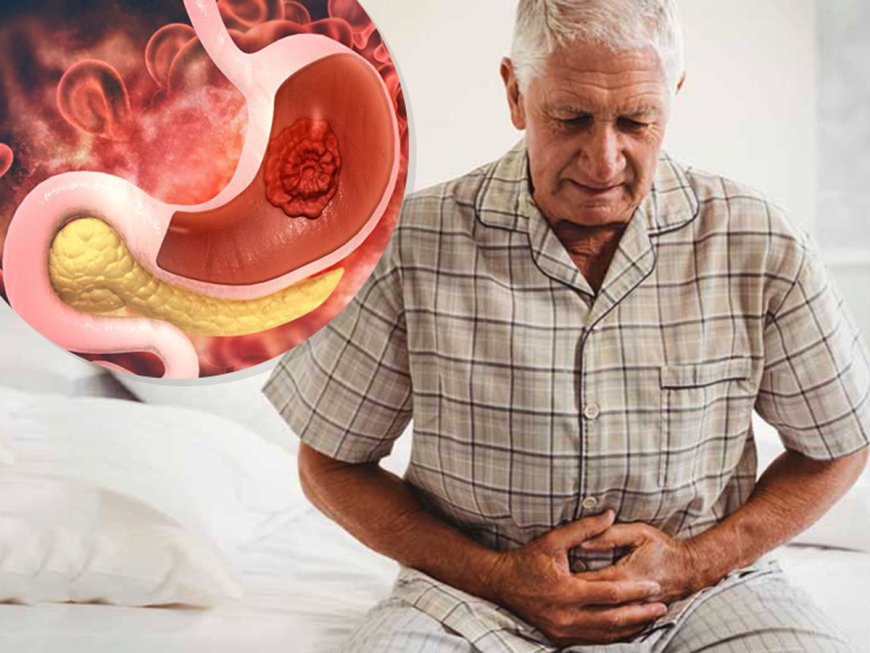
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the cells lining the stomach. It typically develops slowly over many years and can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, and lungs.
Cause
The exact cause of stomach cancer is not always clear, but there are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These risk factors include:
1. Helicobacter pylori infection: This bacterium is a common cause of stomach ulcers and is also linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer.
2. Diet: Consuming a diet high in salty, smoked, or pickled foods, as well as low in fruits and vegetables, may increase the risk of stomach cancer.
3. Family history: Having a family history of stomach cancer or certain inherited genetic conditions, such as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer, can increase the risk of developing the disease.
4. Smoking: Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products can increase the risk of stomach cancer.
5. Age: Stomach cancer is more common in older adults, with the risk increasing after age 50.
6. Gender: Stomach cancer is more common in men than women.
7. Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
It's important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that someone will develop stomach cancer, and some people with no known risk factors may still develop the disease. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help with early detection and treatment of stomach cancer.
Symptoms
Some of the common symptoms of stomach cancer include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
- Feeling full or bloated after eating small amounts of food
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blood in the stool or vomit
There are different types of stomach cancer, including adenocarcinoma, which is the most common type. Treatment options for stomach cancer depend on the stage and location of the cancer, as well as the person's overall health and other factors. Some of the common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
It's important to seek medical attention if you experience any persistent symptoms or changes in your digestive health, as early detection and treatment can improve outcomes for stomach cancer.
Risk factor
A risk factor is anything that increases a person's likelihood of developing a disease. In the case of stomach cancer, there are several factors that can increase the risk of developing the disease. Some of the most common risk factors for stomach cancer include:
1. Age: The risk of stomach cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 50.
2. Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop stomach cancer.
3. Helicobacter pylori infection: This bacterium is a major risk factor for stomach cancer, as it can cause chronic inflammation of the stomach lining that can eventually lead to cancer.
4. Family history: People with a family history of stomach cancer are at increased risk of developing the disease.
5. Previous stomach surgery: People who have had surgery to remove part of their stomach (such as for an ulcer) may be at increased risk of developing stomach cancer.
6. Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for many types of cancer, including stomach cancer.
7. Diet: A diet high in smoked, salted, or pickled foods, as well as low in fruits and vegetables, may increase the risk of stomach cancer.
8. Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
It's important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not mean that someone will definitely develop stomach cancer, and some people without any known risk factors may still develop the disease. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help with early detection and treatment of stomach cancer.
When to see doctor
It's important to see a doctor if you experience any persistent symptoms or changes in your digestive health, as early detection and treatment can improve outcomes for stomach cancer. Some symptoms that may warrant a visit to the doctor include:
1. Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort
2. Feeling full or bloated after eating small amounts of food
3. Nausea and vomiting
4. Loss of appetite
5. Unexplained weight loss
6. Fatigue
7. Blood in the stool or vomit
If you have any of these symptoms, it's important to talk to your doctor as soon as possible. Your doctor may refer you to a gastroenterologist or an oncologist for further evaluation and treatment if necessary.
It's also important to discuss your personal and family medical history with your doctor, especially if you have any known risk factors for stomach cancer, such as a family history of the disease or a history of Helicobacter pylori infection. Your doctor may recommend regular screenings or other preventive measures to help reduce your risk of developing stomach cancer.
Treatment
The treatment for stomach cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the size and location of the tumor, and the person's overall health. Treatment options for stomach cancer may include:
1. Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for stomach cancer and involves removing the tumor and some of the surrounding tissue. In some cases, the entire stomach may need to be removed (gastrectomy).
2. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells and is often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to help shrink the tumor before surgery or to kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery.
3. Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells and is often used in combination with chemotherapy or surgery to treat stomach cancer.
4. Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy involves using drugs that specifically target certain molecules on cancer cells to block their growth and spread.
5. Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy involves using drugs to help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
6. Palliative care: Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life for people with advanced stomach cancer that cannot be cured.
Treatment for stomach cancer can be complex and may involve a team of specialists, including gastroenterologists, surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, and other healthcare professionals. The best treatment plan for an individual with stomach cancer will depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the person's overall health, and their personal preferences.
Complications
Stomach cancer can lead to a number of complications, especially if it is not detected and treated early. Some of the possible complications of stomach cancer include:
1. Metastasis: Stomach cancer can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and bones, which can make it more difficult to treat.
2. Obstruction: A large stomach tumor can obstruct the digestive tract, making it difficult to swallow and leading to vomiting and weight loss.
3. Bleeding: Stomach cancer can cause bleeding in the digestive tract, leading to blood in the stool or vomit.
4. Anemia: Chronic bleeding from stomach cancer can lead to anemia, which is a condition characterized by a low red blood cell count that can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
5. Malnutrition: If stomach cancer makes it difficult to eat or absorb nutrients, malnutrition can occur, which can lead to weakness, weight loss, and other complications.
6. Perforation: In rare cases, a stomach tumor can grow large enough to cause a hole (perforation) in the stomach wall, which can lead to infection and other complications.
It's important to seek medical attention if you experience any persistent symptoms or changes in your digestive health, as early detection and treatment can help prevent complications from stomach cancer.
Conclusion
Stomach cancer is a serious disease that can lead to complications if not detected and treated early. Some of the risk factors for stomach cancer include age, gender, Helicobacter pylori infection, family history, previous stomach surgery, smoking, diet, and obesity. It's important to see a doctor if you experience any persistent symptoms, such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, or blood in the stool or vomit. Treatment options for stomach cancer may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and palliative care. The best treatment plan for an individual with stomach cancer will depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the person's overall health, and their personal preferences. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help with early detection and treatment of stomach cancer, and lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a balanced diet, may help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
What's Your Reaction?