"Cardiomyopathy Research Spotlight: Recent Discoveries And Advancements"
Illuminate recent discoveries and advancements in cardiomyopathy research, offering a glimpse into the cutting-edge developments shaping the future of heart health.
Cardiomyopathy is a complex and often misunderstood disease that affects the heart muscle, leading to impaired function and, in severe cases, heart failure. This condition can manifest in various forms, each presenting unique challenges for patients and healthcare professionals alike.... ("Cardiomyopathy Research Spotlight: Recent Discoveries And Advancements")
Types of Cardiomyopathy:
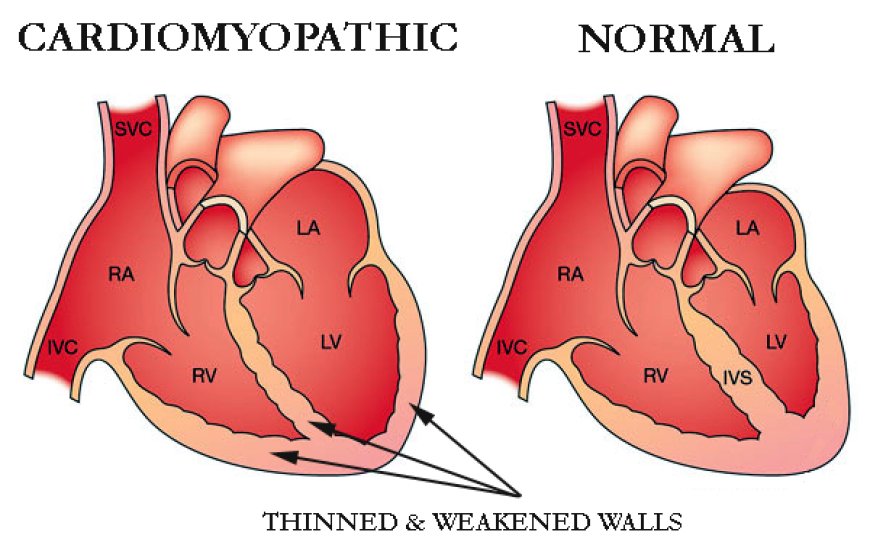
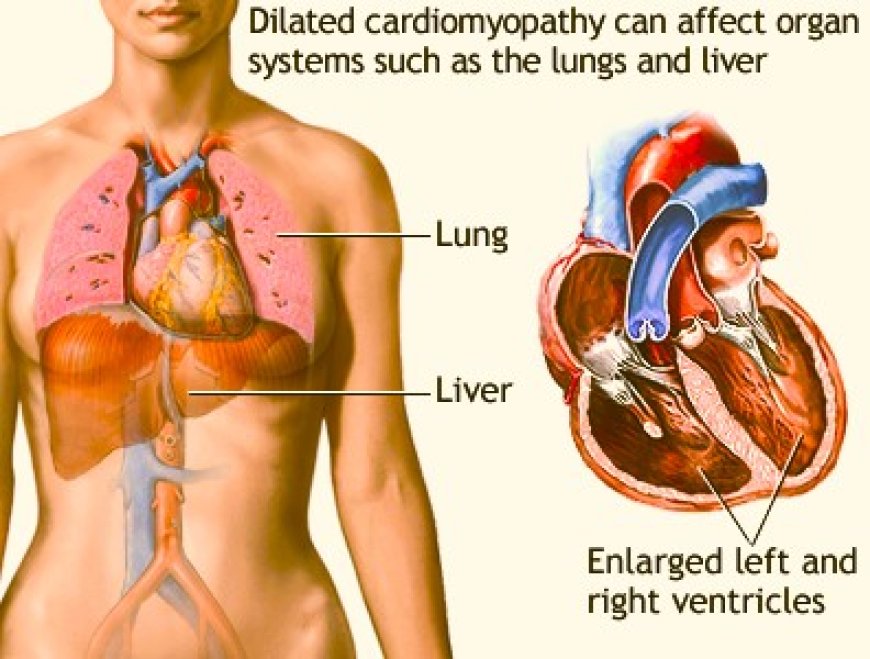
1. Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM): This is the most common type, characterized by an enlarged and weakened heart muscle. As the chambers of the heart dilate, their pumping ability diminishes, affecting blood circulation.
2. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM): In contrast to DCM, HCM involves the thickening of the heart muscle. This can obstruct blood flow and lead to symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
3. Restrictive Cardiomyopathy (RCM): RCM is marked by the stiffening of the heart muscle, restricting its ability to expand and fill with blood. This limitation impairs the heart's efficiency in pumping blood.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Understanding the causes and risk factors for cardiomyopathy is crucial for both prevention and effective management. While the exact etiology can vary, common factors include genetics, viral infections, high blood pressure, and certain toxins.
Genetic Predisposition: Family history plays a significant role in some cases of cardiomyopathy. Individuals with a family history of heart disease should be vigilant about regular check-ups.
Viral Infections: Viruses such as Coxsackie B can infiltrate the heart muscle, triggering inflammation and potentially leading to cardiomyopathy.
Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, gradually weakening the muscle over time.
Toxins: Exposure to certain toxins, such as heavy metals or excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to the development of cardiomyopathy.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Cardiomyopathy often progresses silently, with symptoms appearing gradually. Common signs include fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, and swelling in the legs. Since these symptoms can overlap with other cardiovascular conditions, a thorough diagnostic process is crucial.
Medical History and Physical Examination: Healthcare providers begin by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination to identify potential risk factors and symptoms.
Imaging Tests: Various imaging tests, including echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), provide detailed insights into the structure and function of the heart.
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify potential causes of cardiomyopathy, such as infections or metabolic disorders.
Treatment Option:
The management of cardiomyopathy aims to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve overall quality of life. Treatment strategies may include:
Medications: Prescription drugs, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or diuretics, can help manage symptoms and improve heart function.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, is crucial for managing cardiomyopathy.
Device Therapy: In advanced cases, devices like pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be recommended to regulate heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac death.
Surgical Interventions: In extreme cases, heart transplant surgery might be considered for those with severe and refractory cardiomyopathy.
Living with Cardiomyopathy:
Living with cardiomyopathy requires ongoing care and attention. Patients are advised to:
Attend Regular Follow-ups: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring the disease progression and adjusting treatment plans accordingly.
Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications consistently is crucial to managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Monitor Fluid Intake: Since fluid retention is a common symptom, patients may need to monitor their fluid intake and adhere to dietary restrictions.
Emotional Well-being: Dealing with a chronic
Dealing with a continual circumstance may be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or therapists can help maintain emotional well-being.
Research and Innovations:
Continued research in the field of cardiology has brought forth promising developments. Advancements in genetic testing allow for better identification of individuals at risk due to inherited factors. Precision medicine is emerging as a potential avenue, tailoring treatments based on the specific genetic makeup of the patient.
Stem Cell Therapy: The exploration of stem cell therapy is a frontier in cardiomyopathy research. Scientists are investigating the potential of using stem cells to regenerate damaged heart tissue, offering hope for more effective and targeted treatments.
Telemedicine: Telehealth has become increasingly relevant, providing patients with the opportunity to connect with healthcare professionals remotely. This is especially beneficial for those managing chronic conditions like cardiomyopathy, ensuring regular check-ins without the need for frequent travel.
Global Impact and Awareness:
Cardiomyopathy knows no geographical boundaries, affecting people worldwide. Increasing awareness is crucial for early detection and intervention. National and international initiatives can play a pivotal role in educating the public, promoting healthy lifestyles, and fostering research to uncover new treatment modalities.
Advocacy Organizations: Organizations dedicated to heart health and cardiomyopathy advocacy contribute significantly to raising awareness. They provide resources, support networks, and platforms for sharing experiences.
Public Health Campaigns: Governments and health agencies can implement targeted public health campaigns, educating communities about the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures related to cardiomyopathy.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
Despite progress, challenges persist in the realm of cardiomyopathy. Access to advanced healthcare, especially in lower-income regions, remains a concern. Additionally, the complex nature of the disease requires ongoing collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patients.
Access to Healthcare: Disparities in healthcare access can hinder early diagnosis and optimal management of cardiomyopathy. Addressing these disparities is crucial for ensuring that all individuals, regardless of socioeconomic status, receive timely and effective care.
Research Collaboration: Continued collaboration among researchers worldwide is essential for unlocking the mysteries surrounding cardiomyopathy. By sharing findings and data, the scientific community can accelerate progress and develop more targeted therapies.
Conclusion:
Cardiomyopathy is a multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management. By understanding the various types, causes, and treatment options, both patients and healthcare professionals can work together to mitigate the impact of this condition and enhance the quality of life for those affected. Education, early detection, and proactive care are key in the battle against cardiomyopathy, offering hope for a healthier heart and a brighter future.
What's Your Reaction?