"Detecting Testicular Cancer Early: Your Key To Successful Treatment"
Rally support for Testicular Cancer Awareness Month by spreading information, fostering early detection, and advocating for research advancements.
Testicular cancer is a relatively rare but highly treatable form of cancer that primarily affects young men, typically between the ages of 15 and 35. Despite its low incidence, understanding this disease is crucial for early detection and successful treatment. In this article, we will explore various aspects of testicular cancer, including its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of regular self-exams.
Risk Factors:
Testicular cancer is often considered a disease of young men, with the majority of cases diagnosed in individuals between the ages of 15 and 35. However, it can occur at any age. Several risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing testicular cancer, including a family history of the disease, congenital abnormalities of the testicles, and personal history of testicular cancer. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as undescended testicles, may face an elevated risk.
Signs and Symptoms:
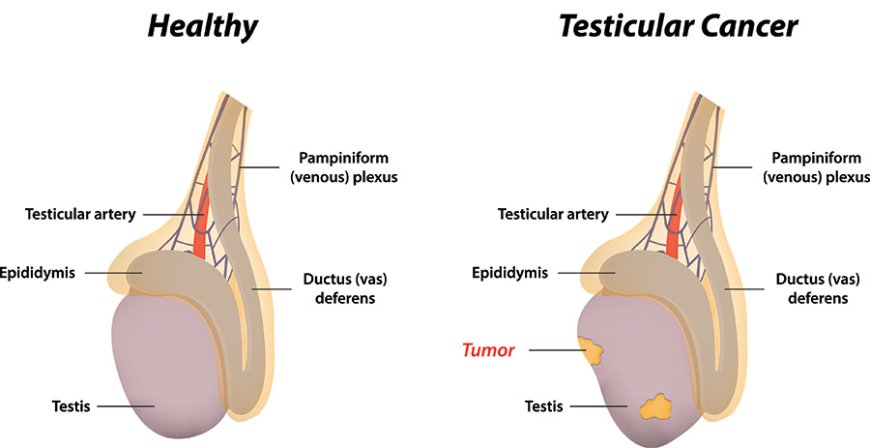
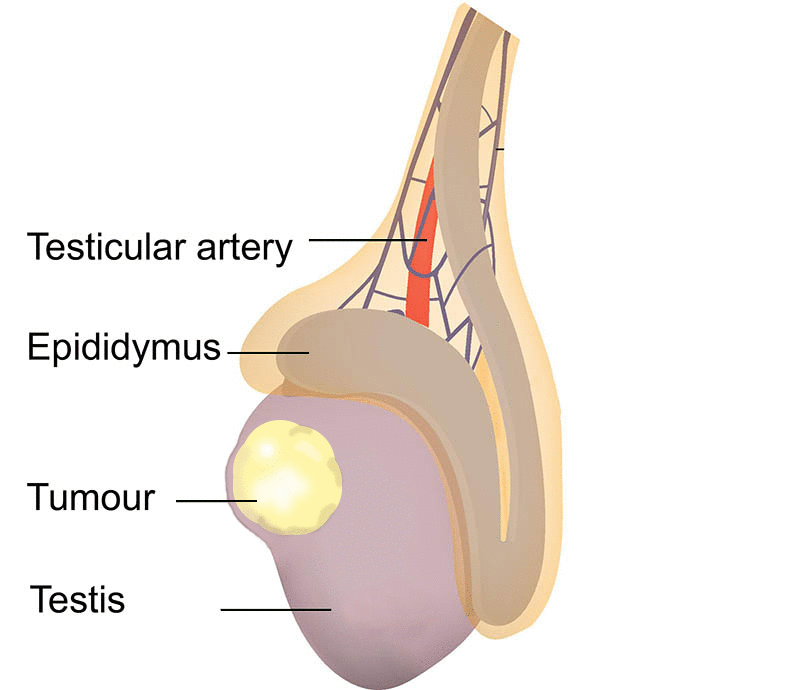
Being aware of the signs and symptoms of testicular cancer is crucial for early detection. Common indicators include a lump or swelling in the testicle, pain or discomfort in the testicle or scrotum, and a feeling of heaviness or change in the size of the testicle. It is essential to note that not all lumps or changes indicate cancer, but any unusual symptoms should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing testicular cancer typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider may conduct a thorough physical examination, checking for any abnormalities in the testicles or surrounding areas. Imaging tests such as ultrasound may be used to visualize the testicles and identify any tumors. Blood tests measuring tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin ( HCG), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), can provide additional diagnostic information.
Treatment Options:
The treatment of testicular cancer depends on several factors, including the type and stage of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. The primary treatment alternatives consist of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. In many cases, surgical removal of the affected testicle, known as a radical inguinal orchiectomy, is the initial step. Following surgery, additional treatments may be recommended based on the specific characteristics of the cancer. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are common adjuvant treatments aimed at eliminating any remaining cancer cells.
Psychosocial Impact:
A testicular cancer diagnosis can have a profound psychosocial impact on individuals. Coping with the emotional aspects of the disease, including anxiety, fear, and uncertainty about the future, is an essential aspect of the overall care for patients. Support groups, counseling, and open communication with healthcare professionals can significantly contribute to managing the emotional challenges associated with testicular cancer.
Importance of Self-Exams:
Regular self-exams are a critical component of testicular cancer awareness and early detection. Men are encouraged to perform self-examinations monthly, ideally after a warm bath or shower when the scrotum is relaxed. Feeling for any changes in size, shape, or consistency of the testicles can help identify abnormalities early on. Prompt reporting of any concerns to a healthcare professional is crucial for timely evaluation and intervention.
Survivorship and Follow-Up:
With advances in medical treatments, the survival rates for testicular cancer are high. Many individuals successfully overcome the disease and go on to lead healthy, fulfilling lives. However, regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor for any potential recurrence or long-term side effects of treatment. Survivorship care plans may include ongoing surveillance, fertility preservation discussions, and addressing any lingering psychological or physical effects of the cancer journey.
Research and Innovations:
Ongoing research in the field of testicular cancer continues to contribute to improvements in diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient outcomes. Innovations in targeted therapies and immunotherapies are being explored to enhance the effectiveness of treatments while minimizing side effects. Understanding the genetic and molecular basis of testicular cancer is opening new avenues for personalized medicine, allowing for more precise and tailored interventions based on individual patient characteristics.
Educational Initiatives:
Educational initiatives play a crucial role in raising awareness about testicular cancer, emphasizing the importance of early detection and dispelling myths surrounding the disease. Public health campaigns, school programs, and community outreach efforts contribute to breaking the stigma associated with discussing reproductive health. Encouraging open conversations about testicular cancer, its symptoms, and the significance of regular self-exams can empower individuals to take charge of their well-being.
Global Impact:
While testicular cancer is more prevalent in certain regions, its impact extends globally. Collaborative efforts between healthcare professionals, researchers, and advocacy groups aim to address disparities in access to healthcare and raise awareness in diverse communities. By fostering a global dialogue on testicular cancer, we can work towards reducing the burden of the disease and ensuring that individuals worldwide have access to timely and effective interventions.
Preventive Measures:
While some risk factors for testicular cancer, such as family history or congenital abnormalities, cannot be controlled, adopting certain lifestyle measures may contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk of cancer. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to general well-being and may have a positive impact on cancer prevention.
Support Networks:
Testicular cancer, like any cancer diagnosis, can be physically and emotionally challenging. Support networks, both online and offline, provide individuals with a platform to share experiences, seek advice, and connect with others facing similar challenges. These networks, often led by survivors and advocacy groups, play a crucial role in fostering a sense of community, reducing isolation, and providing valuable information and resources.
Future Outlook:
The future outlook for testicular cancer is promising, with continued advancements in research, treatment modalities, and supportive care. As scientific understanding deepens, there is hope for even more targeted and effective therapies, further improving outcomes for individuals diagnosed with this form of cancer. Emphasizing the importance of regular screenings, self-exams, and the integration of psychosocial support will remain key components in the comprehensive management of testicular cancer.
Conclusion:
Testicular cancer, while relatively rare, demands attention and understanding. Through a combination of awareness, early detection, evolving treatment options, and robust support networks, we can continue to make significant strides in the fight against this disease. The collaborative efforts of healthcare professionals, researchers, advocacy groups, and individuals themselves contribute to a landscape where testicular cancer is not only treatable but increasingly preventable. By staying informed, proactive, and supportive, we can collectively work towards a future where testicular cancer is a minimal threat to the health and well-being of individuals worldwide.
What's Your Reaction?