"About Meningitis - Everything You Need to Know"
Meningitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection of the membranes around the brain and spinal cord. Learn the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of meningitis.
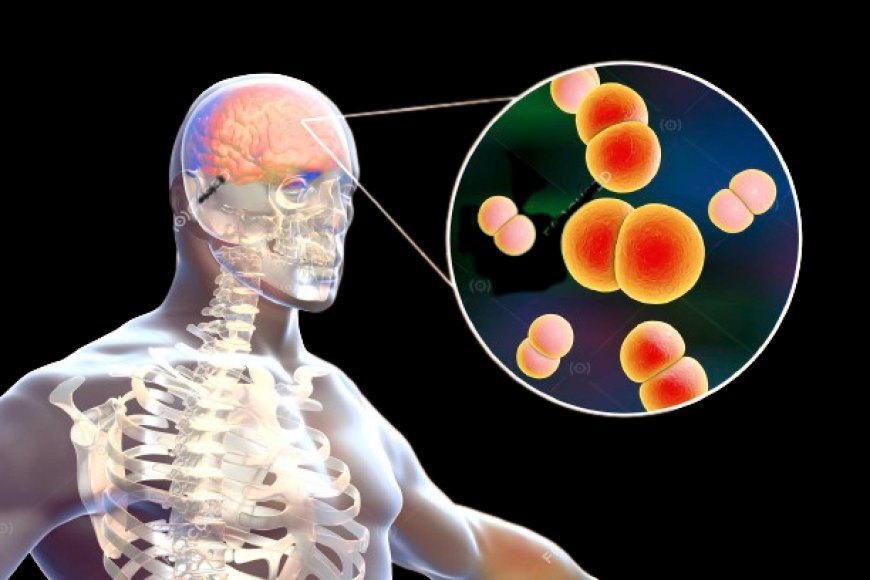
Meningitis is a serious infection that can cause inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The infection can be caused by a virus or bacteria, and it spreads through contact with respiratory or throat secretions from an infected person. Symptoms of meningitis may include fever, headache, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, and confusion. Infants and young children may also experience symptoms such as irritability, lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, and a bulging fontanelle.
Meningitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics or antiviral medications. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide supportive care, such as IV fluids and oxygen therapy. Vaccines are available for certain types of meningitis, including the meningococcal vaccine and the pneumococcal vaccine. These vaccines are recommended for individuals at high risk of developing meningitis, such as college students living in dormitories or individuals with weakened immune systems.
Cause
Meningitis can be caused by a variety of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. The most common causes of meningitis are viral and bacterial infections. Viral meningitis is typically less severe than bacterial meningitis and often resolves on its own within a few weeks. However, bacterial meningitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment with antibiotics to prevent serious complications and death.
The bacteria that commonly cause meningitis include Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenza type B. These bacteria can spread through respiratory or throat secretions from an infected person, such as coughing or sneezing. Bacterial meningitis can also be caused by infections in other parts of the body, such as the ears or sinuses that spread to the brain and spinal cord.
Viral meningitis is usually caused by enteroviruses, which are common during the summer and fall months. Other viruses that can cause meningitis include herpes simplex virus, West Nile virus, and mumps virus.
Fungal and parasitic meningitis are rare but can occur in individuals with weakened immune systems. Fungal meningitis is typically caused by inhaling fungal spores from contaminated soil or bird droppings. Parasitic meningitis is usually caused by exposure to contaminated water or soil.
Symptoms
Symptoms of meningitis can vary depending on the age of the person and the cause of the infection. In some cases, symptoms can develop rapidly and become life-threatening within a matter of hours.
Common symptoms of meningitis include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Stiff neck
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Confusion or altered mental status
- Rash (in some cases)
In infants and young children, symptoms of meningitis may be less specific and can include:
- High-pitched cry or moaning
- Irritability
- Poor feeding or decreased appetite
- Lethargy or difficulty waking up
- Bulging fontanelle (soft spot on the top of the head)
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Meningitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious complications and death.
Risk factors
Anyone can develop meningitis, but certain factors can increase the risk of infection. These risk factors include:
Age: Infants and young children are at higher risk of developing meningitis, as are young adults between the ages of 16 and 25.
Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those undergoing chemotherapy, are at higher risk of developing meningitis.
Exposure to infections: Close contact with someone who has a viral or bacterial infection, such as a cold or strep throat, can increase the risk of developing meningitis.
Crowded living conditions: Living in close quarters with others, such as in college dormitories or military barracks, can increase the risk of meningitis transmission.
Travel: Travel to areas where meningitis is more common, such as sub-Saharan Africa, can increase the risk of infection.
Additionally, certain medical conditions or procedures can increase the risk of meningitis, such as having a cochlear implant or a history of head injury or skull fracture. Vaccination is an effective way to reduce the risk of some types of meningitis.
When to see doctor
It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of meningitis, such as fever, headache, stiff neck, and confusion. Meningitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent serious complications and death.
If you are unsure whether your symptoms may be due to meningitis, you should still seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your healthcare provider can perform a physical examination and order diagnostic tests, such as a lumbar puncture (spinal tap), to determine whether meningitis is present.
If you have been in close contact with someone who has meningitis, or if there has been an outbreak of meningitis in your community or workplace, you should contact your healthcare provider for guidance on whether you need preventive treatment or vaccination.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatments are critical for a good outcome in cases of meningitis.
Prevention
Prevention of meningitis involves taking steps to reduce the risk of infection. Here are some effective prevention measures:
- Vaccination: Vaccines are available for certain types of meningitis, including the meningococcal vaccine and the pneumococcal vaccine. These vaccines are recommended for individuals at high risk of developing meningitis, such as college students living in dormitories or individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Wash hands frequently: Regular hand washing with soap and water, or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, can help prevent the spread of infections that can cause meningitis.
- Cover mouth and nose: Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory infections that can cause meningitis.
- Avoid close contact: Avoid close contact with someone who has a viral or bacterial infection, such as a cold or strep throat.
- Practice good hygiene: Practice good hygiene by keeping your living areas clean and disinfected, and avoiding sharing personal items, such as drinking glasses or utensils.
If you have been exposed to someone with meningitis, your healthcare provider may recommend preventive treatment, such as antibiotics or vaccination, to reduce your risk of infection.
- Meningitis can cause serious complications, even with prompt treatment. These complications can vary depending on the cause of the infection and the age and overall health of the affected person. Here are some possible complications of meningitis:
- Hearing loss: Meningitis can cause permanent hearing loss in some cases, particularly in infants and young children.
- Brain damage: In severe cases of meningitis, the inflammation can lead to brain swelling and damage. This can result in long-term neurological problems, such as seizures, memory loss, and learning disabilities.
- Vision loss: Meningitis can cause permanent vision loss in some cases.
- Septicemia: Meningitis caused by certain types of bacteria, such as Neisseria meningitidis, can lead to septicemia (blood poisoning), which can be life-threatening.
- Hydrocephalus: Meningitis can cause a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, which can lead to hydrocephalus (enlargement of the head) in infants.
It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of meningitis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce the risk of complications and improve the chances of a good outcome.
What's Your Reaction?









































