"Hope on the Horizon: Emerging Therapies in Pancreatic Cancer Research"
Dive into the latest breakthroughs and promising treatments in the world of pancreatic cancer research, offering hope for the future.
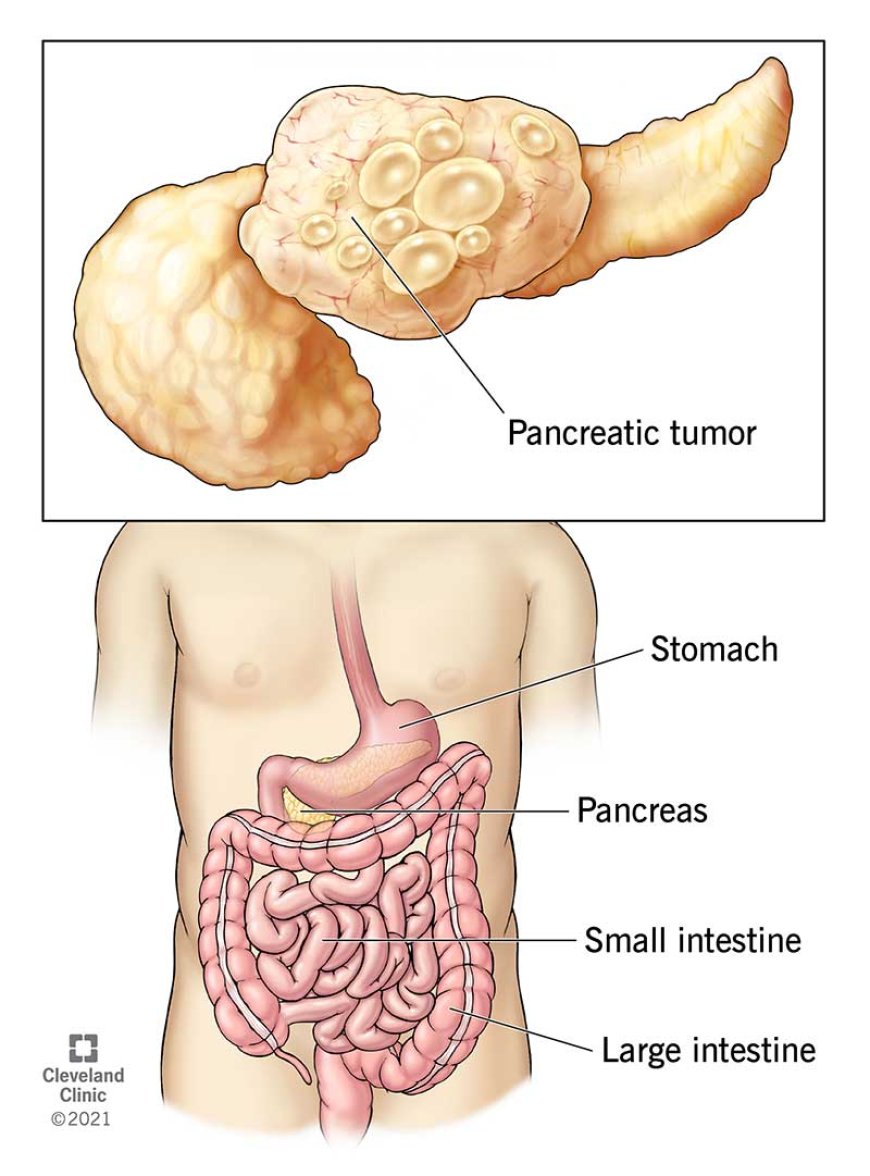
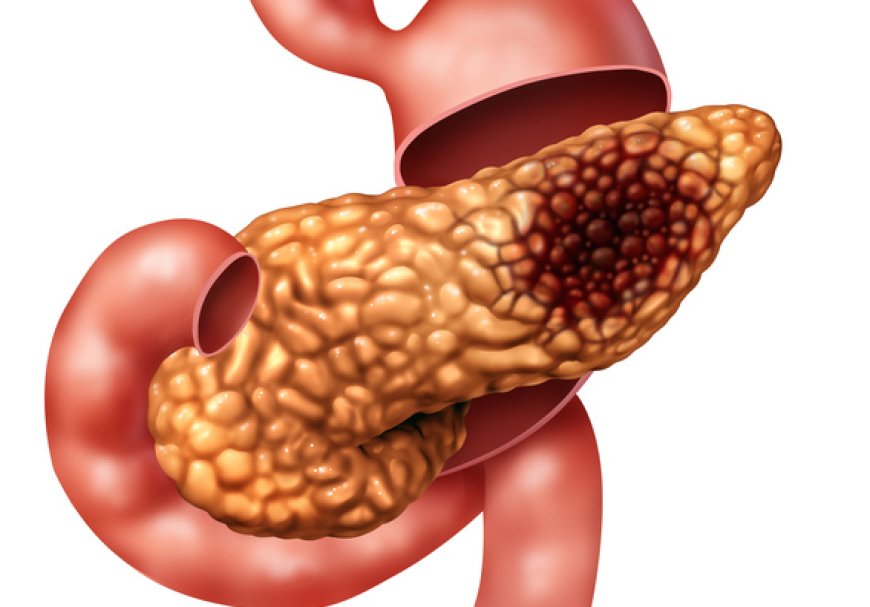
Pancreatic cancer, often referred to as the silent killer, poses a significant challenge in the realm of oncology. This aggressive malignancy originates in the pancreas, a crucial organ located behind the stomach. Despite being relatively rare, pancreatic cancer is notorious for its late-stage diagnosis and high mortality rates. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of pancreatic cancer, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and ongoing research efforts to better understand and combat this formidable adversary.
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer:
The pancreas plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation by producing enzymes and hormones. When cells in the pancreas undergo uncontrolled growth and division, it leads to the formation of a tumor, which can be benign or malignant. Pancreatic cancer is often malignant, meaning it has the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors:
Identifying the risk factors associated with pancreatic cancer is crucial for early detection and prevention. While the exact cause remains elusive, certain factors increase the likelihood of developing this cancer. Age, family history, smoking, obesity, and certain genetic syndromes are among the risk factors. Understanding these elements can help individuals and healthcare professionals in implementing preventive measures and surveillance for those at higher risk.
Symptoms:
One of the challenges in managing pancreatic cancer is its asymptomatic nature in the early stages. Symptoms may only become noticeable when the cancer has advanced, contributing to the late diagnosis and limited treatment options. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, jaundice, unintended weight loss, and changes in stool color. Recognizing these signs and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial for early intervention.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing pancreatic cancer involves a combination of imaging tests, blood tests, and sometimes a biopsy. Computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and endoscopic ultrasound are commonly employed to visualize the pancreas and surrounding structures. Tumor markers in the blood, such as CA 19-9, can provide additional information. Biopsy, obtained through fine-needle aspiration or surgical procedures, confirms the presence of cancer and helps determine its type and stage.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for pancreatic cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and the tumor's characteristics. Surgical removal of the tumor (pancreatic resection) is an option if the cancer is localized and operable. However, due to late-stage diagnoses, surgery is often not feasible. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are commonly used to shrink tumors, relieve symptoms, and potentially improve the chances of surgery. Targeted therapies and immunotherapy are also emerging as promising avenues for treatment.
Challenges in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment:
Pancreatic cancer presents unique challenges for treatment. Its late-stage detection limits the effectiveness of surgery, and the cancer is often resistant to standard chemotherapy. Moreover, the pancreas has a dense structure that can impede drug delivery to the tumor. These challenges highlight the need for innovative approaches and personalized therapies to enhance treatment outcomes.
Research and Innovations:
The urgency of addressing pancreatic cancer has fueled extensive research efforts. Scientists are exploring novel therapies, including precision medicine approaches targeting specific genetic mutations in cancer cells. Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer, is undergoing clinical trials for pancreatic cancer. Early detection methods, such as blood-based biomarkers and advanced imaging technologies, are also under investigation to improve the chances of identifying pancreatic cancer in its initial stages.
Supportive Care and Quality of Life:
Given the aggressive nature of pancreatic cancer, managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients is a crucial aspect of care. Palliative care, which focuses on relieving pain and enhancing comfort, is integrated into the treatment plan. Nutritional support and counseling help patients cope with the physical and emotional challenges associated with the disease.
Patient Advocacy and Awareness:
Raising awareness about pancreatic cancer is essential for early detection and improved outcomes. Patient advocacy groups play a vital role in supporting individuals affected by pancreatic cancer, providing resources, and advocating for research funding. Educational campaigns aim to inform the public about risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of seeking medical attention for early diagnosis.
Genetic Factors and Familial Pancreatic Cancer:
Approximately 5-10% of pancreatic cancer cases have a hereditary component. Families with a history of pancreatic cancer may carry genetic mutations that increase the risk of developing the disease. Understanding these genetic factors is crucial for identifying individuals at higher risk, enabling proactive screening and preventive measures. Genetic counseling and testing play a pivotal role in managing familial pancreatic cancer cases.
Early Detection Strategies:
The lack of specific symptoms in the early stages of pancreatic cancer underscores the importance of developing effective early detection strategies. Researchers are exploring blood-based biomarkers, such as circulating tumor DNA, to identify molecular changes associated with pancreatic cancer. Imaging technologies, including advanced MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, are also being refined to enhance the sensitivity and specificity of detecting small pancreatic tumors.
Clinical Trials and Innovation:
Clinical trials serve as the backbone of advancements in cancer research. Numerous trials are underway to evaluate the effectiveness of novel therapies, combination treatments, and immunotherapeutic approaches for pancreatic cancer. Patients are encouraged to explore participation in clinical trials as these trials not only offer potential access to innovative treatments but also contribute valuable data to inform future treatment strategies.
Patient Empowerment and Survivorship:
Empowering patients with information, support, and resources is integral to their journey with pancreatic cancer. Survivorship programs focus on addressing the physical and emotional needs of individuals after completing treatment. These programs aim to enhance overall well-being, manage potential side effects of treatment, and provide a support system for survivors and their families.
Conclusion:
Pancreatic cancer remains a formidable adversary in the realm of oncology, presenting challenges in early detection and effective treatment. The ongoing efforts of researchers, healthcare professionals, and patient advocacy groups are crucial in unraveling the mysteries surrounding this silent killer. As we continue to advance in understanding the intricacies of pancreatic cancer, there is hope for improved diagnostic tools, innovative therapies, and ultimately, enhanced survival rates for those affected by this disease.
What's Your Reaction?