The Latest Research on Leukemia: Breakthroughs and Innovations
Collaboration and innovation: How researchers, clinicians, and industry are working together to advance leukemia care.
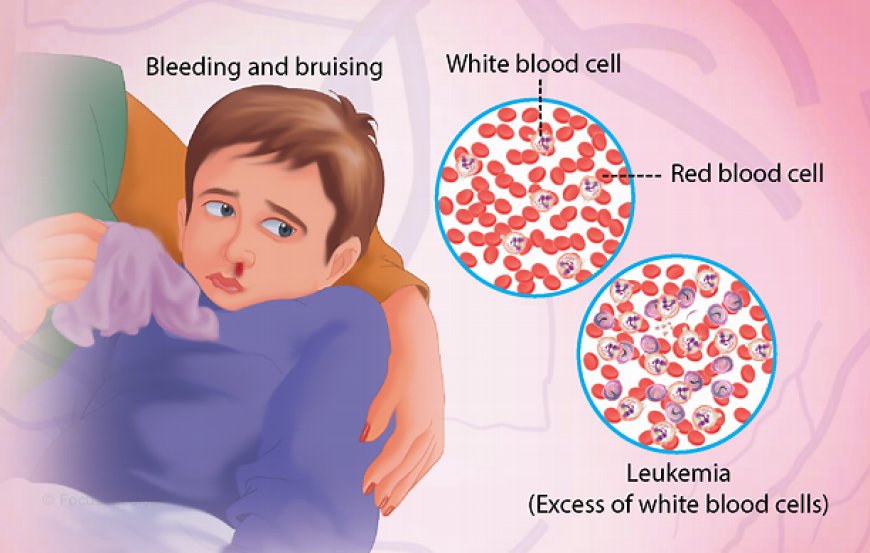
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It occurs when white blood cells are responsible for fighting infection grow uncontrollably and fail to mature properly, As a result the body produces abnormal white blood cells that don't function properly and can't fight infections.
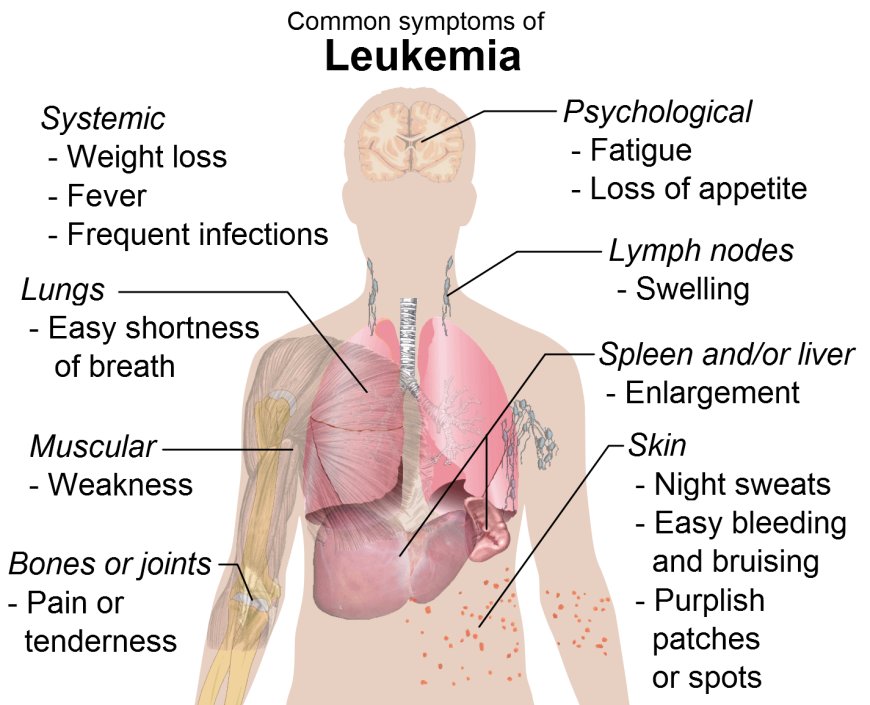
There are several types of leukemia, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myelogenous leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). The symptoms of leukemia can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, but common symptoms include fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and easy bruising or bleeding.
While leukemia can be a serious and life-threatening condition, advances in treatment have led to improved outcomes for many patients. Early detection and timely treatment are key to improving survival rates and achieving remission.
Cause
While the exact cause of leukemia is not fully understood, several factors can increase the risk of developing the disease. These include:
Age: Leukemia can occur at any age, but it's more common in adults over the age of 55.
Gender: Some types of leukemia, such as CLL, are more common in men than women.
Family history: Having a family member with leukemia or another type of blood cancer increases the risk of developing the disease.
Genetic disorders: Certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome and Fanconi anemia, increase the risk of developing leukemia.
Exposure to radiation or chemicals: Exposure to high levels of radiation or certain chemicals, such as benzene, may increase the risk of developing leukemia.
Previous cancer treatment: Previous treatment for cancer with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy may increase the risk of developing leukemia later in life.
It's important to note that having one or more risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop leukemia. Many people with leukemia have no known risk factors. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect and manage any potential risk factors for leukemia.
The symptoms of leukemia can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, but common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Weight loss
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Petechiae (tiny red spots on the skin)
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Joint pain or swelling
- Enlarged lymph nodes, liver, or spleen
- Frequent infections
In acute leukemia, symptoms may appear suddenly and progress quickly, while in chronic leukemias, symptoms may develop slowly over time. Some patients with leukemia may not experience any symptoms at all, and the disease may be discovered during routine blood work.
It's important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of these symptoms, as they can also be caused by other conditions. Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes for patients with leukemia.
When to see doctor
It's important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- If you experience any persistent, unexplained symptoms such as fatigue, fever, night sweats, frequent infections, unexplained weight loss, or unexplained bruising or bleeding.
- If you have known risk factors for leukemia, such as exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, or a family history of leukemia.
- If you have been diagnosed with another blood disorder or cancer and are experiencing new or worsening symptoms.
- If you have received chemotherapy or radiation therapy in the past and are experiencing new or worsening symptoms.
It's important to remember that many of these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions that are not cancer. However, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms and they persist for more than a few weeks, it's important to see your doctor for an evaluation. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and can refer you to a specialist if necessary.
Additionally, if you have any known risk factors for leukemia, such as a family history of the disease, exposure to radiation or chemicals, or a genetic disorder, it's important to discuss this with your healthcare provider and undergo regular check-ups to monitor for any signs of leukemia.
Treatment
Treatment for leukemia depends on several factors, including the type and stage of the disease, the patient's age and overall health, and the presence of certain genetic mutations. The goal of treatment is to eliminate leukemia cells from the body and restore normal blood cell production.
Common treatments for leukemia include:
Chemotherapy: This involves the use of drugs to kill leukemia cells. Chemotherapy can be administered orally or intravenously and may be given in cycles over several months.
Radiation therapy: This uses high-energy radiation to kill leukemia cells. Radiation therapy may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Targeted therapy: This involves the use of drugs that target specific proteins or genetic mutations in leukemia cells. Targeted therapy may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
Stem cell transplant: This involves the replacement of diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. The healthy stem cells may come from a donor or from the patient's own body.
The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the patient's age and overall health, the presence of certain genetic mutations, and the response to previous treatments. Treatment can be intense and may cause side effects, such as hair loss, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
While treatment for leukemia can be challenging, advances in treatment have led to improved outcomes for many patients. Early detection and timely treatment are key to improving survival rates and achieving remission.
Complications
Complications of leukemia can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Common complications include:
Infections: Leukemia can weaken the immune system, making it more vulnerable to infections.
Bleeding and clotting: Abnormal white blood cells can interfere with the body's ability to form blood clots, leading to an increased risk of bleeding or clotting disorders.
Anemia: Leukemia can cause a decrease in red blood cells, leading to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Neutropenia: Neutropenia is a condition in which there are too few neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that fights infection. This can increase the risk of infections.
Organ damage: Leukemia can cause damage to organs such as the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
Additionally, treatment for leukemia can cause its own set of complications, including side effects from chemotherapy or radiation therapy. It's important for patients with leukemia to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage any potential complications and minimize their impact on overall health and quality of life.
Conclusions
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. While the exact cause of leukemia is not fully understood, several factors can increase the risk of developing the disease. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease, but common symptoms include fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and easy bruising or bleeding.
Treatment for leukemia typically involves chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or stem cell transplant. While treatment can be challenging and may cause side effects, advances in treatment have led to improved outcomes for many patients.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect and manage any potential risk factors for leukemia, and early detection and timely treatment are key to improving survival rates and achieving remission. It's important for patients with leukemia to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage any potential complications and minimize their impact on overall health and quality of life.
What's Your Reaction?