MERS-CoV: Analysis of Novel Coronavirus Strains: What We Got Know
MERS-CoV is primarily transmitted from animals to humans, with camels being the primary source of infection, the clinical features of MERS-CoV infection can range from mild respiratory illness to severe acute respiratory illness, which can lead to death
In recent years, the world has witnessed the emergence of several novel coronavirus strains that have posed a significant threat to public health. One of these strains is the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), which was first reported in Saudi Arabia in 2012. Since then, the virus has caused several outbreaks in the Middle East and other parts of the world. In this article, we will discuss the characteristics of MERS-CoV, its mode of transmission, clinical features, and prevention measures.
What is MERS-CoV?
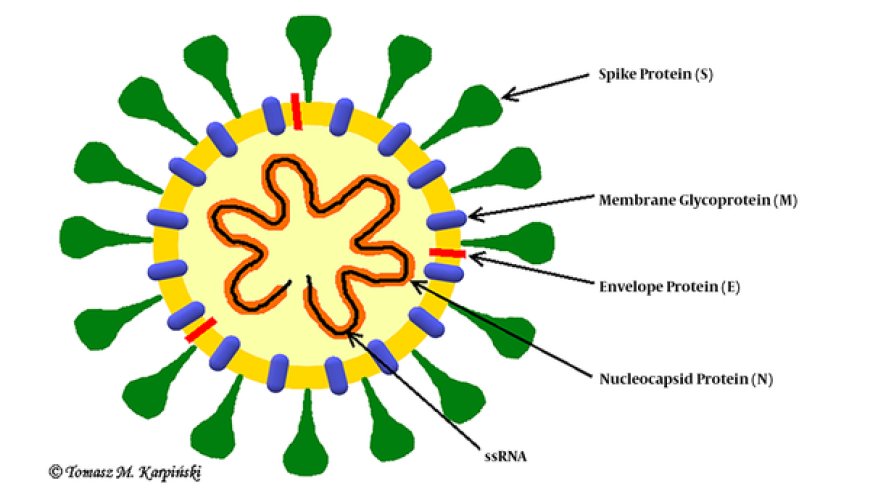
MERS-Co V is a novel coronavirus strain that belongs to the same family as the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the coronavirus responsible for the current COVID-19 pandemic. The virus was first identified in a patient from Saudi Arabia who presented with symptoms of respiratory illness in 2012. Since then, there have been several outbreaks of MERS-CoV in the Middle East, with sporadic cases reported in other parts of the world.
Mode of Transmission
MERS-CoV is primarily transmitted from animals to humans, with camels being the primary source of infection. However, human-to-human transmission can occur through close contact with an infected person. The virus can spread through respiratory secretions, such as coughing and sneezing, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces. Health workers are at a higher risk of infection due to their close contact with infected patients.
Clinical Features
The clinical features of MERS-CoV infection can range from mild respiratory illness to severe acute respiratory illness, which can lead to death. The symptoms of MERS-CoV infection include fever, cough, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, the virus can cause pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and kidney failure. The mortality rate of MERS-CoV is estimated to be around 35%, which is higher than that of other coronavirus strains.
Prevention Measures
Preventing the spread of MERS-CoV requires a multi-pronged approach that includes public health measures, personal protective measures, and clinical management. Public health measures such as early detection, isolation of infected patients, contact tracing, and quarantine are essential in containing outbreaks. Personal protective measures, such as wearing masks, hand hygiene, and avoiding close contact with sick people, can help prevent transmission.
Clinical management of MERS-CoV includes supportive care such as oxygen therapy and fluid management, as there is currently no specific antiviral treatment available. Vaccines and antiviral drugs are currently being developed, but their efficacy and safety are yet to be established.
MERS-CoV Outbreaks
MERS-CoV has caused several outbreaks since it was first identified in 2012. The largest outbreak occurred in Saudi Arabia in 2014 and spread to other countries, including South Korea, where it caused significant panic and resulted in over 180 confirmed cases and 36 deaths. Since then, there have been sporadic cases reported in various countries, including the United States, France, and the United Kingdom. The most recent outbreak occurred in Saudi Arabia in 2019, with six confirmed cases reported.
Research on MERS-CoV
Since its emergence in 2012, researchers have been studying MERS-CoV to better understand the virus and develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. Studies have shown that the virus has several unique features, such as its ability to infect a broad range of human cells, including those in the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and urinary tracts.
Scientists have also identified several potential targets for antiviral drugs and vaccines, including the virus's spike protein, which it uses to enter human cells. Several experimental vaccines and antiviral drugs have been developed, but their efficacy and safety are yet to be established.
Challenges in Controlling MERS-CoV
One of the challenges in controlling MERS-CoV is its ability to infect camels, which can act as a reservoir for the virus. This makes it difficult to eradicate the virus completely. Another challenge is the lack of awareness and understanding of the virus among the general public, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment. In addition, the lack of a specific treatment for the virus makes it challenging to manage severe cases.
Conclusion
MERS-CoV is a novel coronavirus strain that has caused several outbreaks since it was first identified in 2012. The virus primarily spreads through contact with infected animals, especially camels, but human-to-human transmission can also occur. Early detection, isolation, and quarantine of infected patients, coupled with personal protective measures, are essential in preventing the spread of the virus. Public health authorities and healthcare providers must remain vigilant in monitoring and responding to MERS-CoV outbreaks to prevent the virus from becoming a global threat.
Research on the virus is ongoing, and scientists are working to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. While there is still much to learn about MERS-CoV, increased awareness and understanding of the virus can help in preventing and controlling future outbreaks.
What's Your Reaction?