The Connection Between Pneumonia and Chronic Illnesses: What You Need to Know
Pneumonia can also be caused by non-infectious factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Some common causes of pneumonia include…..
Overall:
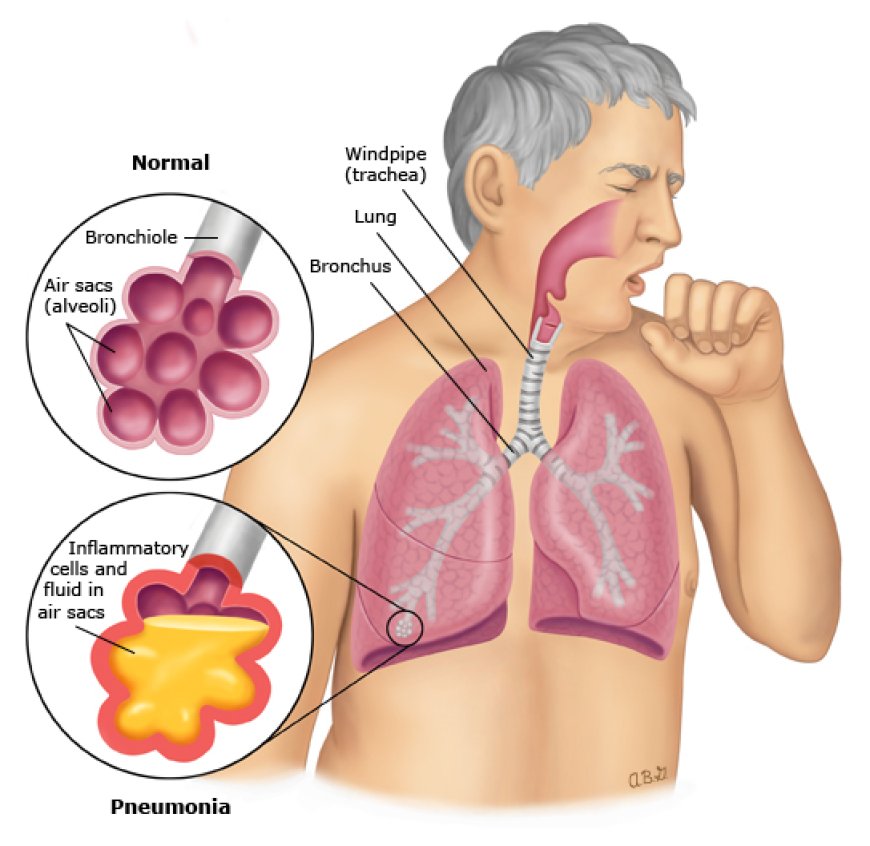
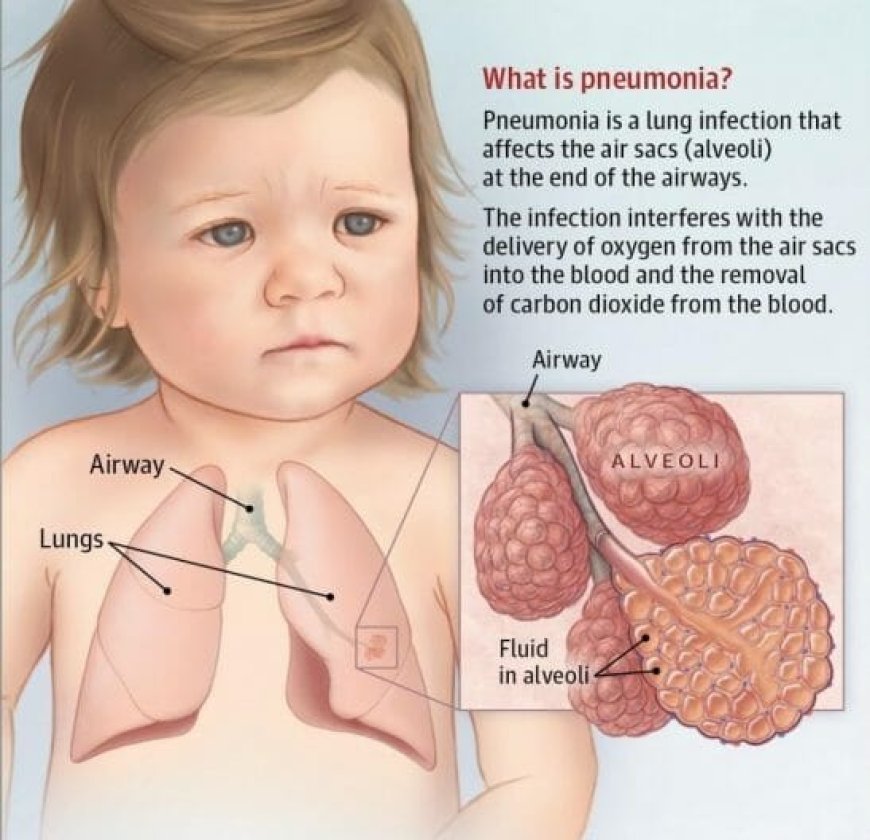
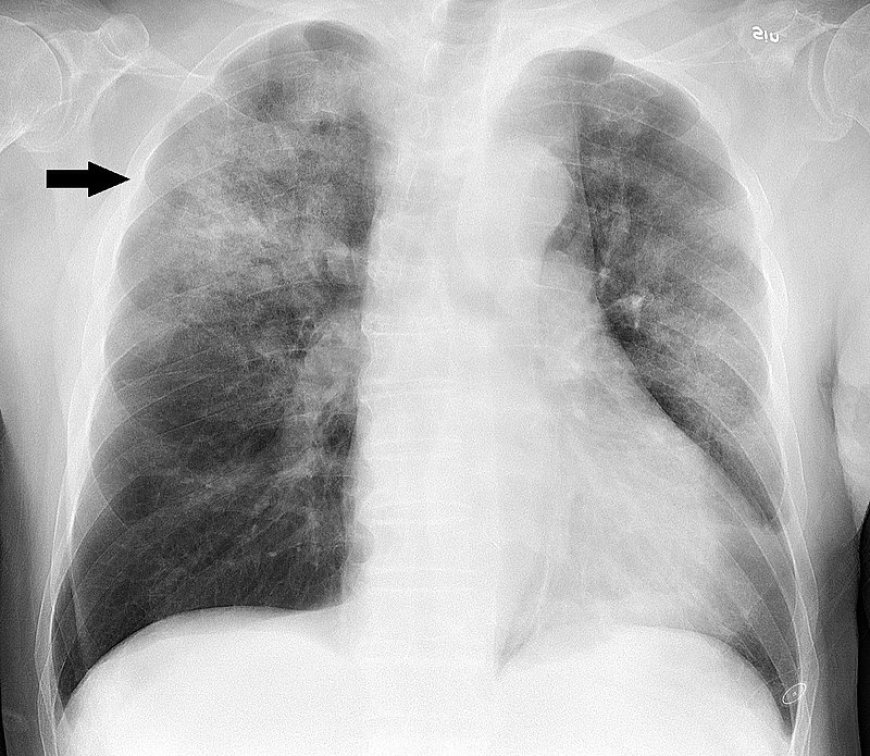
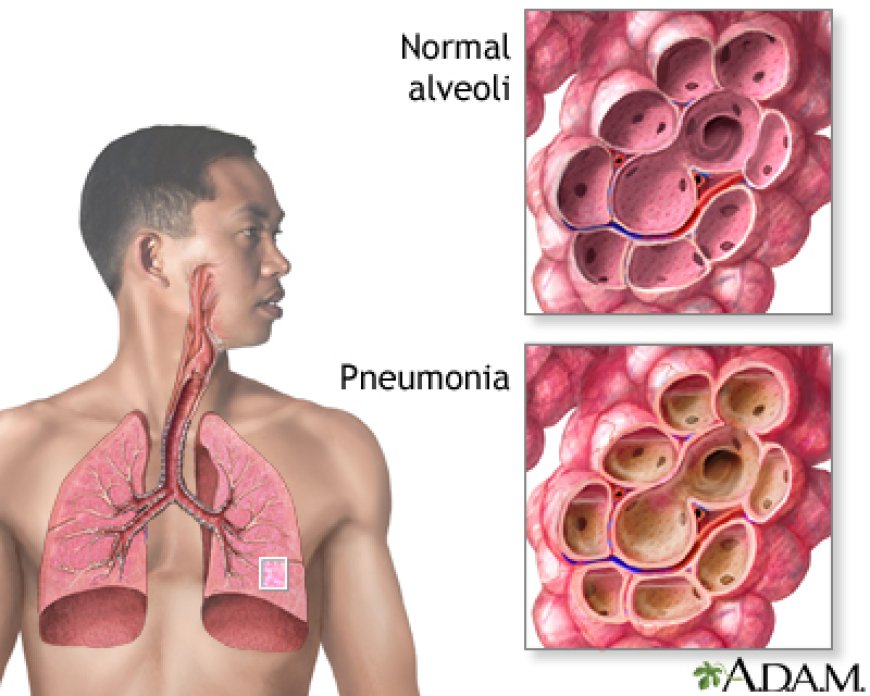
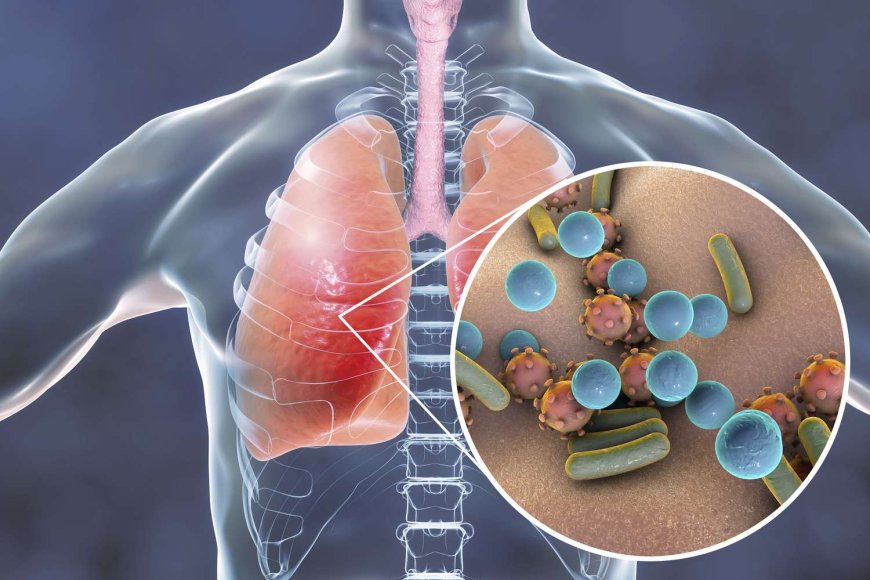
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can cause inflammation in one or both lungs. It is caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and can be life-threatening, particularly for older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatments of pneumonia, and provide helpful tips for preventing its onset.
Symptoms of pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can be vary depending on the type of organism causing the infection, the age and overall health of the person infected, and the severity of the infection. Some common symptoms of pneumonia include:
1. Coughing that produces phlegm or mucus
2. Shortness of breath
3. Fever and chills
4. Chest pain
5. Fatigue and weakness
6. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to more serious complications, such as sepsis or respiratory failure.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Some common causes of pneumonia include:
1. Streptococcus pneumoniae
2. Haemophilus influenzae
3. Legionella pneumophila
4. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
5. Influenza virus
Pneumonia can also be caused by non-infectious factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals, smoke inhalation, and aspiration of food or other substances into the lungs.
Treatments for Pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia will vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Mild cases of pneumonia can often be treated with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers. More severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics or antiviral medications. In some cases, supplemental oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation may be necessary to help the patient breathe.
Preventing Pneumonia
Preventing pneumonia is an important part of maintaining good health, particularly for people with weakened immune systems or other risk factors. Some tips for preventing pneumonia include:
1. Getting vaccinated against pneumococcal bacteria and influenza
2. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently and avoiding close contact with sick people
3. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke
4. Eating a healthy diet and staying physically active to boost your immune system
5. Getting enough rest and managing stress to reduce your risk of infection
Certainly! Here is more information on pneumonia and how to prevent it.
Preventing Pneumonia in Children
Children are more susceptible to developing pneumonia due to their underdeveloped immune systems. Therefore, parents and caregivers should take extra precautions to prevent its onset. Some tips for preventing pneumonia in children include:
1. Making sure they receive the recommended pneumococcal and influenza vaccines
2. Encouraging them to wash their hands frequently and avoid touching their face
3. Ensuring they get plenty of rest, eat a healthy diet, and stay physically active
4. Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke and other harmful pollutants
5. Keeping them away from sick individuals and ensuring they receive prompt medical attention if they develop any symptoms of pneumonia
Preventing Pneumonia in Older Adults
Older adults are also at increased risk of developing pneumonia due to their weakened immune systems and higher likelihood of having other chronic health conditions. Therefore, taking steps to prevent pneumonia is crucial for their overall health and well-being. Some tips for preventing pneumonia in older adults include:
1. Ensuring they receive the recommended pneumococcal and influenza vaccines
2. Encouraging them to wash their hands frequently and avoid touching their face
3. Helping them stay physically active and eat a healthy diet
4. Encouraging them to quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
5. Seeking prompt medical attention if they develop any symptoms of pneumonia or other respiratory infections
In addition to these preventive measures, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of pneumonia and seek medical attention immediately if you or a loved one experience any of them. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
Risk factors
Pneumonia is a severe respiratory infection that affects the lungs, leading to inflammation in the air sacs. This condition can affect anyone, but certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing pneumonia. In this article, we will discuss the risk factors associated with pneumonia.
Age
One of the primary risk factors for pneumonia is age. The elderly and young children are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia than other age groups. This is because their immune systems are weaker, making it harder for them to fight off infections. It is essential to take extra precautions to protect these vulnerable populations from contracting pneumonia.
Smoking
Smoking is another significant risk factor for pneumonia. It weakens the immune system and damages the lungs, making it easier for bacteria and viruses to cause infection. Additionally, smoking damages the cilia, tiny hair-like structures in the lungs that help sweep out mucus and bacteria. This can lead to a build-up of mucus and bacteria, increasing the risk of developing pneumonia.
Chronic Medical Conditions
People with chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or lung disease, are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia. These conditions weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections. If you have a chronic medical condition, it is important to take extra precautions to protect yourself from contracting pneumonia.
Weakened Immune System
A weakened immune system is another significant risk factor for pneumonia. Certain medical conditions, such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, or autoimmune disorders, can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing pneumonia. Additionally, treatments such as chemotherapy or organ transplantation can weaken the immune system, making it easier to contract pneumonia.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also increase the risk of developing pneumonia. Exposure to pollutants or chemicals in the air can damage the lungs and weaken the immune system. People who live in crowded or unsanitary conditions are also at a higher risk of developing pneumonia.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that can be caused by a variety of infectious agents. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of pneumonia, take steps to prevent its onset, and seek medical attention promptly if you develop any symptoms. By following these tips, you can help protect yourself and your loved ones from the potentially life-threatening effects of pneumonia.
What's Your Reaction?